The 3-month readmission rate remains unacceptably high in a large North American cohort of patients with cirrhosis
- PMID: 26690389
- PMCID: PMC4700508
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.28414
The 3-month readmission rate remains unacceptably high in a large North American cohort of patients with cirrhosis
Abstract
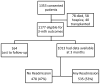
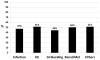
In smaller single-center studies, patients with cirrhosis are at a high readmission risk, but a multicenter perspective study is lacking. We evaluated the determinants of 3-month readmissions among inpatients with cirrhosis using the prospective 14-center North American Consortium for the Study of End-Stage Liver Disease cohort. Patients with cirrhosis hospitalized for nonelective indications provided consent and were followed for 3 months postdischarge. The number of 3-month readmissions and their determinants on index admission and discharge were calculated. We used multivariable logistic regression for all readmissions and for hepatic encephalopathy (HE), renal/metabolic, and infection-related readmissions. A score was developed using admission/discharge variables for the total sample, which was validated on a random half of the total population. Of the 1353 patients enrolled, 1177 were eligible on discharge and 1013 had 3-month outcomes. Readmissions occurred in 53% (n = 535; 316 with one, 219 with two or more), with consistent rates across sites. The leading causes were liver-related (n = 333; HE, renal/metabolic, and infections). Patients with cirrhosis and with worse Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score or diabetes, those taking prophylactic antibiotics, and those with prior HE were more likely to be readmitted. The admission model included Model for End-Stage Liver Disease and diabetes (c-statistic = 0.64, after split-validation 0.65). The discharge model included Model for End-Stage Liver Disease, proton pump inhibitor use, and lower length of stay (c-statistic = 0.65, after split-validation 0.70). Thirty percent of readmissions could not be predicted. Patients with liver-related readmissions consistently had index-stay nosocomial infections as a predictor for HE, renal/metabolic, and infection-associated readmissions (odds ratio = 1.9-3.0).
Conclusions: Three-month readmissions occurred in about half of discharged patients with cirrhosis, which were associated with cirrhosis severity, diabetes, and nosocomial infections; close monitoring of patients with advanced cirrhosis and prevention of nosocomial infections could reduce this burden. (Hepatology 2016;64:200-208).
© 2015 by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
Comment in
-
Challenge accepted: Confronting readmissions for our patients with cirrhosis.Hepatology. 2016 Jul;64(1):26-8. doi: 10.1002/hep.28471. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26806609 No abstract available.
References
-
- Fontanarosa PB, McNutt RA. Revisiting hospital readmissions. JAMA. 2013;309:398–400. - PubMed
-
- Benbassat J, Taragin M. Hospital readmissions as a measure of quality of health care: advantages and limitations. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160:1074–1081. - PubMed
-
- Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States Part III: Liver, biliary tract, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1134–1144. - PubMed
-
- Kanwal F, Volk M, Singal A, Angeli P, Talwalkar J. Improving quality of health care for patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:1204–1207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical