Molecular Characterization and Biological Effects of a C-Type Lectin-Like Receptor in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)
- PMID: 26690423
- PMCID: PMC4691118
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms161226175
Molecular Characterization and Biological Effects of a C-Type Lectin-Like Receptor in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)
Abstract
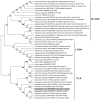
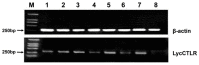
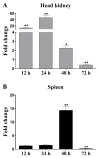
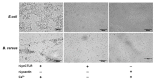
The C-type lectin-like receptors (CTLRs) play important roles in innate immunity as one type of pattern recognition receptors. Here, we cloned and characterized a C-type lectin-like receptor (LycCTLR) from large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. The full-length cDNA of LycCTLR is 880 nucleotides long, encoding a protein of 215 amino acids. The deduced LycCTLR contains a C-terminal C-type lectin-like domain (CTLD), an N-terminal cytoplasmic tail, and a transmembrane region. The CTLD of LycCTLR possesses six highly conserved cysteine residues (C1-C6), a conserved WI/MGL motif, and two sugar binding motifs, EPD (Glu-Pro-Asp) and WYD (Trp-Tyr-Asp). Ca(2+) binding site 1 and 2 were also found in the CTLD. The LycCTLR gene consists of five exons and four introns, showing the same genomic organization as tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and guppy (Poecilia retitculata) CTLRs. LycCTLR was constitutively expressed in various tissues tested, and its transcripts significantly increased in the head kidney and spleen after stimulation with inactivated trivalent bacterial vaccine. Recombinant LycCTLR (rLycCTLR) protein produced in Escherichia coli BL21 exhibited not only the hemagglutinating activity and a preference for galactose, but also the agglutinating activity against two food-borne pathogenic bacteria E. coli and Bacillus cereus in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. These results indicate that LycCTLR is a potential galactose-binding C-type lectin that may play a role in the antibacterial immunity in fish.
Keywords: C-type lectin-like receptor; antibacterial immunity; bacterial agglutination; hemagglutination; large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel C-type lectin, Nattectin-like protein, with a wide range of bacterial agglutination activity in large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Mar;50:231-41. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.01.032. Epub 2016 Jan 30. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26828263
-
Molecular and immune response characterizations of IL-6 in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Mar;50:263-73. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.01.041. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26868214
-
Molecular characterization and expression analysis of a complement component C3 in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Feb;42(2):272-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2014.11.006. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25463300
-
Latrophilin, an adhesion GPCR with galactose-binding lectin domain involved in the innate immune response of Tribolium castaneum.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 2):126707. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126707. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37673160 Review.
-
Evolution of animal lectins.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1998;19:45-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-48745-3_3. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1998. PMID: 15898188 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Comprehensive Insights into the Early Immune Response of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Induced by Trivalent Bacterial Vaccine.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 30;12(1):e0170958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170958. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28135311 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

