Secreted Factors from Human Vestibular Schwannomas Can Cause Cochlear Damage
- PMID: 26690506
- PMCID: PMC4686978
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18599
Secreted Factors from Human Vestibular Schwannomas Can Cause Cochlear Damage
Abstract
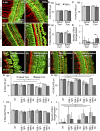
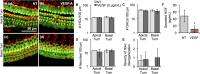
Vestibular schwannomas (VSs) are the most common tumours of the cerebellopontine angle. Ninety-five percent of people with VS present with sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL); the mechanism of this SNHL is currently unknown. To establish the first model to study the role of VS-secreted factors in causing SNHL, murine cochlear explant cultures were treated with human tumour secretions from thirteen different unilateral, sporadic VSs of subjects demonstrating varied degrees of ipsilateral SNHL. The extent of cochlear explant damage due to secretion application roughly correlated with the subjects' degree of SNHL. Secretions from tumours associated with most substantial SNHL resulted in most significant hair cell loss and neuronal fibre disorganization. Secretions from VSs associated with good hearing or from healthy human nerves led to either no effect or solely fibre disorganization. Our results are the first to demonstrate that secreted factors from VSs can lead to cochlear damage. Further, we identified tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) as an ototoxic molecule and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) as an otoprotective molecule in VS secretions. Antibody-mediated TNFα neutralization in VS secretions partially prevented hair cell loss due to the secretions. Taken together, we have identified a new mechanism responsible for SNHL due to VSs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Sporadic vestibular schwannomas associated with good hearing secrete higher levels of fibroblast growth factor 2 than those associated with poor hearing irrespective of tumor size.Otol Neurotol. 2013 Jun;34(4):748-54. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e31828048ec. Otol Neurotol. 2013. PMID: 23512073 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from human vestibular schwannomas associated with poor hearing damage cochlear cells.Neuro Oncol. 2016 Nov;18(11):1498-1507. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now099. Epub 2016 May 18. Neuro Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27194145 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma knife radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: results of hearing preservation in relation to the cochlear radiation dose.Laryngoscope. 2009 Jun;119(6):1076-81. doi: 10.1002/lary.20245. Laryngoscope. 2009. PMID: 19399836
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1: A novel treatment for the protection or regeneration of cochlear hair cells.Hear Res. 2015 Dec;330(Pt A):2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.04.009. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Hear Res. 2015. PMID: 25937136 Review.
-
Hearing Outcomes After Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Vestibular Schwannomas : Mechanism of Hearing Loss and How to Preserve Hearing.Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2016;(43):3-36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-21359-0_1. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26508404 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for inflammation in normal-appearing brain regions in patients with growing sporadic vestibular schwannoma: A PET study.Neurooncol Adv. 2024 Jun 8;6(1):vdae094. doi: 10.1093/noajnl/vdae094. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Neurooncol Adv. 2024. PMID: 38962752 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation mediates noise-induced synaptic imbalance and tinnitus in rodent models.PLoS Biol. 2019 Jun 18;17(6):e3000307. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000307. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31211773 Free PMC article.
-
The vestibular calyceal junction is dismantled following subchronic streptomycin in rats and sensory epithelium stress in humans.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Jul;97(7):1943-1961. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03518-z. Epub 2023 May 17. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37195449 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine Profiling of Cyst Fluid and Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Cystic Vestibular Schwannoma.Otol Neurotol. 2023 Dec 1;44(10):1073-1081. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000004032. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Otol Neurotol. 2023. PMID: 37853737 Free PMC article.
-
Cochlear signal intensity changes in vestibular schwannoma: a balanced fast field-echo MRI study.Front Neurol. 2025 May 19;16:1549869. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1549869. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40458464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mahaley M. S. Jr., Mettlin C., Natarajan N., Laws E. R. Jr. & Peace B. B. Analysis of patterns of care of brain tumor patients in the United States: a study of the Brain Tumor Section of the AANS and the CNS and the Commission on Cancer of the ACS. Clin. Neurosurg. 36, 347–352 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Aronzon A., Ruckenstein M. J. & Bigelow D. C. The efficacy of corticosteroids in restoring hearing in patients undergoing conservative management of acoustic neuromas. Otol. Neurotol. 24, 465–468 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Nadol J. B. Jr., Diamond P. F. & Thornton A. R. Correlation of hearing loss and radiologic dimensions of vestibular schwannomas (acoustic Neuromas). Am. J. Otol. 17, 312–316 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

