Parent-only interventions for childhood overweight or obesity in children aged 5 to 11 years
- PMID: 26690844
- PMCID: PMC8761478
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012008
Parent-only interventions for childhood overweight or obesity in children aged 5 to 11 years
Abstract
Background: Child and adolescent overweight and obesity have increased globally, and are associated with short- and long-term health consequences.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy of diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions delivered to parents only for the treatment of overweight and obesity in children aged 5 to 11 years.
Search methods: We performed a systematic literature search of databases including the Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO, CINAHL and LILACS as well trial registers. We checked references of identified trials and systematic reviews. We applied no language restrictions. The date of the last search was March 2015 for all databases.
Selection criteria: We selected randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions delivered to parents only for treating overweight or obesity in children aged 5 to 11 years.
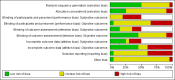
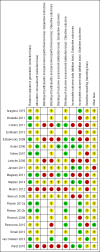
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trials for risk of bias and evaluated overall study quality using the GRADE instrument. Where necessary, we contacted authors for additional information.
Main results: We included 20 RCTs, including 3057 participants. The number of participants ranged per trial between 15 and 645. Follow-up ranged between 24 weeks and two years. Eighteen trials were parallel RCTs and two were cluster RCTs. Twelve RCTs had two comparisons and eight RCTs had three comparisons. The interventions varied widely; the duration, content, delivery and follow-up of the interventions were heterogeneous. The comparators also differed. This review categorised the comparisons into four groups: parent-only versus parent-child, parent-only versus waiting list controls, parent-only versus minimal contact interventions and parent-only versus other parent-only interventions.Trial quality was generally low with a large proportion of trials rated as high risk of bias on individual risk of bias criteria.In trials comparing a parent-only intervention with a parent-child intervention, the body mass index (BMI) z score change showed a mean difference (MD) at the longest follow-up period (10 to 24 months) of -0.04 (95% confidence interval (CI) -0.15 to 0.08); P = 0.56; 267 participants; 3 trials; low quality evidence. In trials comparing a parent-only intervention with a waiting list control, the BMI z score change in favour of the parent-only intervention at the longest follow-up period (10-12 months) had an MD of -0.10 (95% CI -0.19 to -0.01); P = 0.04; 136 participants; 2 trials; low quality evidence. BMI z score change of parent-only interventions when compared with minimal contact control interventions at the longest follow-up period (9 to 12 months) showed an MD of 0.01 (95% CI -0.07 to 0.09); P = 0.81; 165 participants; 1 trial; low quality evidence. There were few similarities between interventions and comparators across the included trials in the parent-only intervention versus other parent-only interventions and we did not pool these data. Generally, these trials did not show substantial differences between their respective parent-only groups on BMI outcomes.Other outcomes such as behavioural measures, parent-child relationships and health-related quality of life were reported inconsistently. Adverse effects of the interventions were generally not reported, two trials stated that there were no serious adverse effects. No trials reported on all-cause mortality, morbidity or socioeconomic effects.All results need to be interpreted cautiously because of their low quality, the heterogeneous interventions and comparators, and the high rates of non-completion.
Authors' conclusions: Parent-only interventions may be an effective treatment option for overweight or obese children aged 5 to 11 years when compared with waiting list controls. Parent-only interventions had similar effects compared with parent-child interventions and compared with those with minimal contact controls. However, the evidence is at present limited; some of the trials had a high risk of bias with loss to follow-up being a particular issue and there was a lack of evidence for several important outcomes. The systematic review has identified 10 ongoing trials that have a parent-only arm, which will contribute to future updates. These trials will improve the robustness of the analyses by type of comparator, and may permit subgroup analysis by intervention component and the setting. Trial reports should provide adequate details about the interventions to be replicated by others. There is a need to conduct and report cost-effectiveness analyses in future trials in order to establish whether parent-only interventions are more cost-effective than parent-child interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
EL: none known.
LAK: none known.
RJ: none known.
WR: none known.
JC: none known.
EM: none known.
LE: none known.
MIM: none known.
KR: none known.
Figures
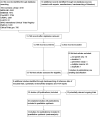











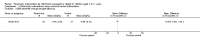
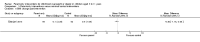



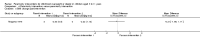
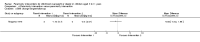
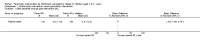
References
References to studies included in this review
Aragona 1975 {published data only}
Boutelle 2011 {published data only}
Collins 2011 {published data only}
-
- Burrows T, Janet WM, Collins CE. Long‐term changes in food consumption trends in overweight children in the HIKCUPS intervention. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 2011;53(5):543‐7. - PubMed
-
- Burrows T, Warren JM, Baur LA, Collins CE. Impact of a child obesity intervention on dietary intake and behaviors. International Journal of Obesity 2008;32(10):1481‐8. - PubMed
-
- Burrows T, Warren JM, Collins CE. The impact of a child obesity treatment intervention on parent child‐feeding practices. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2010;5(1):43‐50. - PubMed
-
- Cliff DP, Okely AD, Morgan PJ, Steele JR, Jones RA, Colyvas K, et al. Movement skills and physical activity in obese children: randomized controlled trial. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 2011;43(1):90‐100. - PubMed
-
- Collins CE, Morgan PJ, Okely AD, Burrows TL, Cliff DP, Jones RA, et al. HIKCUPS (Hunter Illawarra Kids Challenge Using Parent Support) reduces BMI z‐score up to 2 years: results of a multi‐site randomized trial for overweight children. Obesity Reviews 2010;11:280.
Esfarjani 2013 {published data only}
Estabrooks 2009 {published data only}
-
- Estabrooks PA, Shoup JA, Gattshall M, Dandamudi P, Shetterly S, Xu S. Automated telephone counseling for parents of overweight children: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal Preventive Medicine 2009;26(1):35‐42. - PubMed
Golan 2006 {published data only}
-
- Golan M. Parents as agents of change in childhood obesity ‐ from research to practice. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2006;1:66‐76. - PubMed
-
- Golan M, Kaufman V, Shahar DR. Childhood obesity treatment: targeting parents exclusively v. parents and children. British Journal of Nutrition 2006;95:1008‐15. - PubMed
Golley 2007 {published data only}
-
- Golley RK, Magarey AM, Baur LA, Steinbeck KS, Daniels LA. Twelve‐month effectiveness of a parent‐led, family‐focused weight‐management program for prepubertal children: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2007;119(3):517‐25. - PubMed
-
- Golley RK, Magarey AM, Daniels LA. Children's food and activity patterns following a six‐month child weight management program. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2011;6:409‐14. - PubMed
Janicke 2008 {published data only}
-
- Janicke DM, Sallinen BJ, Perri MG, Lutes LD, Huerta M, Silverstein JH, et al. Comparison of parent‐only versus family‐based interventions for overweight children in underserved rural settings: outcomes from Project STORY. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2008;162:1119‐25. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Walker K. Mechanisms of self‐esteem change in overweight children participating in a family‐based weight management program. Dissertation. University of Florida. 2007.
Jansen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jansen E, Mulkens S, Jansen A. Tackling childhood overweight: treating parents exclusively is effective. International Journal of Obesity (Lond) 2011;35(4):501‐9. - PubMed
Magarey 2011 {published data only}
-
- Magarey AM, Perry RA, Baur LA, Steinbeck KS, Sawyer M, Hills AP, et al. A parent‐led family‐focused treatment program for overweight children aged 5 to 9 years: the PEACH RCT. Pediatrics 2011;127(2):214‐22. - PubMed
Mazzeo 2014 {published data only}
Moens 2012 {published data only}
-
- Moens E, Braet C. Training parents of overweight children in parenting skills: a 12‐month evaluation. Behaviour. 2012;40(1):1‐18. - PubMed
Munsch 2008 {published data only}
-
- Munsch S, Roth B, Michael T, Meyer AH, Biedert E, Roth S, et al. Randomized controlled comparison of two cognitive behavioral therapies for obese children: mother versus mother‐child cognitive behavioral therapy. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics 2008;77:235‐46. - PubMed
-
- Roth B, Munsch S, Meyer AH. Long‐term evaluation of a psychological training for obese children and their parents (TAKE) [Langzeitevaluation eines psychologischen Trainingsfür adipöse Kinder und ihre Eltern (TAKE)]. Praxis der Kinderpsychologie und Kinderpsychiatrie 2011;60:304‐21. - PubMed
Raynor 2012a {published data only}
Raynor 2012b {published data only}
Resnick 2009 {published data only}
-
- Resnick EA, Bishop M, O'Connell A, Hugo B, Isern G, Timm A, et al. The CHEER study to reduce BMI in Elementary School students: a school‐based, parent‐directed study in Framingham, Massachusetts. Journal of School Nursing 2009;25(5):361‐72. - PubMed
Resnicow 2015 {published data only}
Small 2013 {published data only}
-
- Small L, Bonds‐McClain D. A primary care‐based randomized treatment trial with overweight/obese children. Communicating Nursing Research 2013;46:291.
van Grieken 2013 {published data only}
West 2010 {published data only}
-
- West F, Sanders MR, Cleghorn GJ, Davies PS. Randomised clinical trial of a family‐based lifestyle intervention for childhood obesity involving parents as the exclusive agents of change. Behaviour Research and Therapy 2010;48(12):1170‐9. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Berry 2007 {published data only}
Biotnott 2009 {published data only}
-
- Boitnott AD. Childhood obesity: development of a parent‐focused intervention. Dissertation Abstracts International: Section B: The Sciences and Engineering 2009;7(3):1588.
Bohlin 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bohlin A, Klaesson S, Kowalski J. Can telephone consultations substitute visits in treatment of childhood obesity? Results from a randomized trial. Obesity Facts 2012;5:237.
De Bock 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bock F, Genser B, Raat H, Fischer JE, Renz‐Polster H. A participatory physical activity intervention in preschools: a cluster randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2013;45(1):64‐74. - PubMed
Dewes 2014 {published data only}
-
- Dewes O, Sluyter J, Scragg R, Jiang Y, Percival T. Fanau FAB: parent‐focused weight management programme for Pacific children. Obesity Reviews 2014;15:212.
Hendrie 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hendrie GA, Golley RK. A parent led intervention targeting purchase of low fat dairy foods reduces saturated fat intake without a change in energy, BMI or negative food consequences. Obesity Research and Clinical Practice 2011;5:S28.
Hystad 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hystad HT, Steinsbekk S, Ødegard R, Wichstrøm L, Gudbrandsen OA. A randomised study on the effectiveness of therapist‐led v. self‐help parental intervention for treating childhood obesity. British Journal of Nutrition 2013;110:1143‐50. - PubMed
John 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- John R. Effects of Parent‐Focused Media Interventions on Body Mass Index, Waist Size, Self‐Perception, Family Eating Habits, and Family Activity Habits in Overweight Hispanic Children [Thesis]. New York: Teachers College, Columbia University, 2009.
Lawson 2015 {published data only}
-
- Lawson Health Research. FOR HEALTH: a family‐oriented healthy eating, activity and lifestyle intervention for overweight preschool children, 2015. ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT01698606 (accessed 16 December 2015).
Le Gross 2006 {published data only}
-
- The "Kids on Track" program, 2006. www.anzctr.org.au/ACTRN12606000382572.aspx (accessed 15 December 2015).
NHLBI 2008 {published data only}
-
- National Heart Lung Blood Institute. Family‐based nutrition intervention for Latino children, 2008. ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT00224887 (accessed 15 December 2015).
Parra‐Medina 2015 {published data only}
-
- University of Texas Health Science Center. Health4Kids intervention trial for Hispanic families, 2015. ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02343367 (accessed 15 December 2015).
Shelton 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shelton D, LeGros K, Norton L, Stanton‐Cook S, Morgan J, Masterman P. Randomised controlled trial: a parent‐based group education programme for overweight children. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2007;43:799‐805. - PubMed
Steele 2014 {published data only}
-
- Steele RG, Jensen CD, Gayes LA, Liebold HC. Medium is the message: moderate parental control of feeding correlates with improved weight outcome in a pediatric obesity intervention. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2014;39(7):708‐17. - PubMed
Volkenant 2011 {published data only}
-
- Volkenant KR, Quinlan NP, Ubinger M, Rukstalis M, Cochran WJ. Early childhood obesity intervention in primary care: parent stress levels and child mental health symptoms. Obesity 2011;19:S108.
Warschburger 2013 {published data only}
-
- Warschburger P, Kroller K, Unverzagt S, Haerting J. What is the parents' part in long‐term weight management of their obese child? Results from the EPOC study. Obesity Facts 2013;6:230.
-
- Warschburger P, Kroller K, Unverzagt S, Haerting J, Egmond‐Fröhlich A. Empowering parents of obese children (EPOC): a randomized‐controlled trial on additional long‐term weight effects of a parent training. Submitted data. - PubMed
-
- Warschburger P, Kuhne D, Kroller K. Do parents influence the long term development of obese children's weight? First results of the EPOC‐study [in German]. Padiatrische Praxis 2012;79(2):185‐92.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Geronilla 1981 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Geronilla LS. A study of weight control in pediatric obesity using mothers as behavior modifiers. Dissertation Abstracts International 1981;42(5‐B):2027.
Gillick 1975 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Gillick SL. Training parents as therapists in the treatment of juvenile obesity. Dissertation Abstracts International 1975;35(10‐B):5111‐2.
Golan 1998 {published data only}
-
- Golan M, Crow S. Targeting parents exclusively in the treatment of childhood obesity: long‐term results. Obesity Research 2004;12:357‐61. - PubMed
-
- Golan M, Fainaru M, Weizman A. Role of behaviour modification in the treatment of childhood obesity with the parents as the exclusive agents of change. International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders 1998;22:1217‐24. - PubMed
-
- Golan M, Weizman A, Apter A, Fainaru M. Parents as the exclusive agents of change in the treatment of childhood obesity. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1998;67(6):1130‐5. - PubMed
-
- Golan M, Weizman A, Fainaru M. Impact of treatment for childhood obesity on parental risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Preventive Medicine 1999;29(6):519‐26. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Ball 2012 {published data only}
Dalton 2011 {published data only}
Gerards 2012 {published data only}
Janicke 2011 {published data only}
NCT01197443 {published data only}
-
- Acronym: PAAC. Ongoing study Study start date: November 2010 Study completion date: July 2015.
NCT01546727 {published data only}
-
- Acronym: Behavioral Treatment for Obese Preschoolers (LAUNCH). Ongoing study Study start date: March 2012 Study completion date: November 2016.
NCT01552642 {published data only}
-
- Acronym: none. Ongoing study Study start date: February 2013 Study completion date: August 2015.
NCT01792531 {published data only}
-
- Acronym: More and Less study (M+L). Ongoing study Study start date: January 2013 Study completion date: December 2017.
NCT02373670 {published data only}
-
- Acronym: none. Ongoing study Study start date: January 2015 Study completion date: June 2015.
Önnerfält 2012 {published data only}
-
- Önnerfält J, Erlandsson LK, Orban K, Broberg M, Helgason C, Thorngren‐Jerneck K. A family‐based intervention targeting parents of preschool children with overweight and obesity: conceptual framework and study design of LOOPS ‐ Lund Overweight and Obesity Preschool Study. BMC Public Health 2012;12:879. - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Beller 2013
Bocca 2013
-
- Bocca G, Ongering EC, Stolk RP, Sauer PJ. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk factors in 3‐ to 5‐year old overweight or obese children. Hormone Research in Paediatrics 2013;80(3):201‐6. - PubMed
Clark 2007
-
- Clark HR, Goyder E, Bissell P, Blank L, Peters J. How do parents' child feeding behaviours influence child weight? Implications for childhood obesity policy. Journal of Public Health 2007;29:132‐41. - PubMed
CMO 2012
-
- Chief Medical Officer. Annual report of the Chief Medical Officer: surveillance volume, 2012: on the State of the Public's Health. www.gov.uk/government/publications/chief‐medical‐officer‐annualreport‐su... (accessed 30 March 2015).
Cole 2000
Cole 2012
-
- Cole TJ, Lobstein T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut‐offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatric Obesity 2012;7(4):284‐94. - PubMed
Daniels 2009
-
- Daniels SR. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity 2009;33(Suppl 1):S60‐5. - PubMed
de Onis 2010
-
- Onis M, Blössner M. Borghi E. Global prevalence and trends of overweight and obesity among preschool children. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92(5):1257‐64. - PubMed
Eady 2008
Egan 2013
Egbewale 2014
Ells 2015
-
- Ells LJ, Hancock C, Copley VR, Mead E, Dinsdale H, Kinra S, et al. Prevalence of severe childhood obesity in England: 2006‐2013. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2015;100(7):631‐6. - PubMed
Ewald 2014
-
- Ewald H, Kirby J, Rees K, Robertson W. Parent‐only interventions in the treatment of childhood obesity: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Public Health 2014;36(3):476‐89. - PubMed
Faith 2012
-
- Faith MS, Horn L, Appel LJ, Burke LE, Carson JAS, Franch HA, et al. AHA scientific statement: evaluating parents and adult caregivers as "Agents of Change" for treating obese children: evidence for parent behavior change strategies and research gaps: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2012;125:1186‐207. - PubMed
Follman 1992
-
- Follmann D, Elliot P, Suh I, Cutler J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1992;45(7):769‐73. - PubMed
Freedman 2006
-
- Freedman DS, Khan LK, Serdula MK, Ogden CL, Dietz WH. Racial and ethnic differences in secular trends for childhood BMI, weight, and height. Obesity 2006;14(2):301‐8. - PubMed
Glenny 1997
-
- Glenny AM, O'Meara S, Melville A, Sheldon TA, Wilson C. The treatment and prevention of obesity: a systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 1997;21(9):715‐37. - PubMed
Golan 2004
-
- Golan M, Crow S. Targetting parents exclusively in the treatment of childhood obesity: long‐term results. Obesity Research 2004;12:357‐61. - PubMed
Griffiths 2010
-
- Griffiths LJ, Parsons TJ, Hill AJ. Self‐esteem and quality of life in obese children and adolescents: a systematic review. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2010;5(4):282‐304. - PubMed
Gustafson 2006
-
- Gustafson SL, Rhodes RE. Parental correlates of physical activity in children and early adolescents. Sports Medicine 2006;36:79‐97. - PubMed
Halliday 2014
-
- Halliday JA, Palma CL, Mellor D, Green J, Renzaho AMN. The relationship between family functioning and child and adolescent overweight and obesity: a systematic review. International Journal of Obesity 2014;38:480‐93. - PubMed
Higgins 2002
-
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1539‐58. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2009
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
Hróbjartsson 2013
-
- Hróbjartsson A, Thomsen AS, Emanuelsson F, Tendal B, Hilden J, Boutron I, et al. Observer bias in randomized clinical trials with measurement scale outcomes: a systematic review of trials with both blinded and nonblinded assessors. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2013;185(4):E201‐11. - PMC - PubMed
HSCIC 2015
-
- Health and Social Care Information Centre. National Child Measurement Programme ‐ England, 2012‐13 school year. www.hscic.gov.uk/catalogue/PUB13115 (accessed 30 March 2015).
Jang 2015
Jull 2013
-
- Jull A, Chen R. Parent‐only vs. parent‐child (family‐focused) approaches for weight loss in obese and overweight children: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Obesity Reviews 2013;14:761‐8. - PubMed
Kelly 2013
-
- Kelly AS, Barlow SE, Rao G, Inge TH, Hayman LL, Steinberger J, et al. Severe obesity in children and adolescents: identification, associated health risks, and treatment approaches: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013;128(15):1689‐712. - PubMed
Kirkham 2010
Knai 2012
Leclercq 2013
-
- Leclercq E, Leeflang MM, Dalen EC, Kremer LC. Validation of search filters for identifying pediatric studies in PubMed. Journal of Pediatrics 2013;162(3):629‐34. - PubMed
Liberati 2009
Lobstein 2004
-
- Lobstein T, Baur L, Uauy R. Obesity in children and young people: a crisis in public health. Obesity Reviews 2004;5(Suppl 1):4‐104. - PubMed
Meader 2014
Narang 2012
Ng 2014
NICE 2013
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Managing overweight and obesity among children and young people: lifestyle weight management services. NICE Guidelines PH47, 2013. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ph47 (accessed 15 December 2015).
Noo NHS 2011
-
- National Obesity Observatory on behalf of the Public Health Observatories in England. A simple guide to classifying body mass index in children, 2011. www.noo.org.uk/uploads/doc/vid_11601_A_simple_guide_to_classifying_BMI_i... (accessed 3 November 2015).
Ogden 2006
-
- Ogden J, Reynolds R, Smith A. Expanding the concept of parental control: a role for overt and covert control in children's snacking behaviour?. Appetite 2006;47:100‐6. - PubMed
Olds 2011
-
- Olds T, Maher C, Zumin S, Péneau S, Lioret S, Castetbon K, et al. Evidence that the prevalence of childhood overweight is plateauing: data from nine countries. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2011;6(5‐6):342‐60. - PubMed
Oude Luttikhuis 2009
Parsons 1999
-
- Parsons TJ, Power C, Logan S, Summerbell CD. Childhood predictors of adult obesity: a systematic review. International Journal of Obesity 1999;23(Suppl 8):S1‐107. - PubMed
Paulis 2014
-
- Paulis WD, Silva S, Koes BW, Middelkoop M. Overweight and obesity are associated with musculoskeletal complaints as early as childhood: a systematic review. Obesity Reviews 2014;15(1):52‐67. - PubMed
Puhl 2007
-
- Puhl RM, Latner JD. Stigma, obesity, and the health of the nation's children. Psychology Bulletin 2007;133(4):557‐80. - PubMed
Rajput 2014
-
- Rajput N, Tuohy P, Mishra S, Smith A, Taylor B. Overweight and obesity in 4‐5‐year‐old children in New Zealand: results from the first 4 years (2009‐2012) of the B4 School Check programme. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2014;51(3):334‐43. - PubMed
Reilly 2003
Reilly 2011
-
- Reilly JJ, Kelly J. Long‐term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. International Journal of Obesity 2011;35(7):891‐8. - PubMed
Riley 2011
-
- Riley RD, Higgins JP, Deeks JJ. Interpretation of random effects meta‐analyses. BMJ 2011;342:d549. - PubMed
Rokholm 2010
-
- Rokholm B, Baker JL, Sørenson TI. The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999 ‐ a review of evidence and perspectives. Obesity Reviews 2010;11(12):835‐46. - PubMed
Shrewsbury 2008
-
- Shrewsbury V, Wardle J. Socioeconomic status and adiposity in childhood: a systematic review of cross‐sectional studies 1990‐2005. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16(2):275‐84. - PubMed
Singh 2008
-
- Singh AS, Mulder C, Twisk JW, vanMechelen W, Chinapaw MJ. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obesity Reviews 2008;9(5):474‐88. - PubMed
Skinner 2014
-
- Skinner AC, Skelton JA. Prevalence and trends in obesity and severe obesity among children in the United States, 1999‐2012. JAMA Pediatrics 2014;168(6):561‐6. - PubMed
Sleddens 2011
-
- Sleddens EF, Gerards SM, Thijs C, Vries NK, Kremers SP. General parenting, childhood overweight and obesity‐inducing behaviors: a review. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity 2011;6:e12‐27. - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JA, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JP, Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta‐analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011;343:d4002. - PubMed
Tang‐Peronard 2008
-
- Tang‐Peronard JL, Heitmann BL. Stigmatization of obese children and adolescents, the importance of gender. Obesity Reviews 2008;9(6):522‐34. - PubMed
Upton 2012
-
- Upton D, Upton P, Bold J, Peters DM. Regional evaluation of weight management programmes for children and families, 2012. www.obesitywm.org.uk/resources/Worcester_Report_Fina.pdf (accessed 15 December 2015).
Wang 2012
Wansink 2006
-
- Wansink B. Nutritional gatekeepers and the 72% solution. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2006;106:1324‐7. - PubMed
Whitaker 1997
-
- Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH. Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. New England Journal of Medicine 1997;337(13):869‐73. - PubMed
WHO 2015a
-
- World Health Organization. Fact sheet on overweight and obesity. www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en (accessed 30 March 2015).
WHO 2015b
-
- World Health Organization. The WHO Child Growth Standards. www.who.int/childgrowth/publications/technical.report.pub/en/ (accessed 30 March 2015).
Wong 2006a
Wong 2006b
-
- Wong SS, Wilczynski NL, Haynes RB. Optimal CINAHL search strategies for identifying therapy studies and review articles. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2006;38(2):194‐9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

