Efficient chemo-enzymatic gluten detoxification: reducing toxic epitopes for celiac patients improving functional properties
- PMID: 26691232
- PMCID: PMC4686914
- DOI: 10.1038/srep18041
Efficient chemo-enzymatic gluten detoxification: reducing toxic epitopes for celiac patients improving functional properties
Abstract
Protein engineering of gluten, the exogenous effector in celiac disease, seeking its detoxification by selective chemical modification of toxic epitopes is a very attractive strategy and promising technology when compared to pharmacological treatment or genetic engineering of wheat. Here we present a simple and efficient chemo-enzymatic methodology that decreases celiac disease toxic epitopes of gluten proteins improving its technological value through microbial transglutaminase-mediated transamidation of glutamine with n-butylamine under reducing conditions. First, we found that using low concentrations of amine-nucleophile under non-reducing conditions, the decrease in toxic epitopes is mainly due to transglutaminase-mediated cross-linking. Second, using high amine nucleophile concentrations protein cross-linking is substantially reduced. Third, reducing conditions increase 7-fold the transamidation reaction further decreasing toxic epitopes amount. Fourth, using n-butylamine improves gluten hydrophobicity that strengthens the gluten network. These results open the possibility of tailoring gluten for producing hypoallergenic flours while still taking advantage of the unique viscoelastic properties of gluten.
Figures
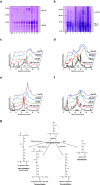
 F;
F;  FK-C2H5;
FK-C2H5;  FB 5X;
FB 5X;  FB 50X;
FB 50X;  FmTG;
FmTG;  F + mTG. Or, under reducing conditions. (i):
F + mTG. Or, under reducing conditions. (i):  FR;
FR;  FRB 50X;
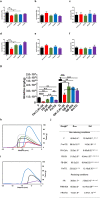
FRB 50X;  FRmTG. (j) Rheological properties of dough prepared from wheat flour, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing and reducing conditions. #For sample nomenclature please consult Fig. 6. The columns values with the same letter are not statistically significant, p < 0.05 (n = 2).
FRmTG. (j) Rheological properties of dough prepared from wheat flour, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with K-C2H5 and n-butylamine as amine nucleophiles under non-reducing and reducing conditions. #For sample nomenclature please consult Fig. 6. The columns values with the same letter are not statistically significant, p < 0.05 (n = 2).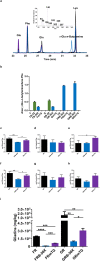
 FR,
FR,  FRB 50X and
FRB 50X and  FRmTG. Indicated are the peaks of glutamic acid (Glu), phenylalanine (Phe), glutamine (Gln), γ-glutamyl-n-butylamine (γ-Glu-n-butylamine) and lysine (Lys). EI mass spectra of γ-Glu-n-butylamine residue is shown. (b) γ-Glu-n-butylamine residue formation under non-reducing and reducing conditions. For b, experiments were run in triplicate, and error bars represent the s.d. Amino acid composition determined after enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat flour (c–e) and gluten (f–h), original and derivatised with mTG alone and with n-butylamine as amine nucleophile under reducing conditions. For (c–h), error bars represent the standard deviation *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001 (n = 3). (i) R5 reactive epitopes’ content (mg of gliadin per kg of product) of wheat flour and gluten, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with n-butylamine as amine nucleophile under reducing conditions after peptic-tryptic digestion. n = 2 different experiments (each with four replicates) and error bars represent the s.d. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. For sample nomenclature please consult Fig. 6.
FRmTG. Indicated are the peaks of glutamic acid (Glu), phenylalanine (Phe), glutamine (Gln), γ-glutamyl-n-butylamine (γ-Glu-n-butylamine) and lysine (Lys). EI mass spectra of γ-Glu-n-butylamine residue is shown. (b) γ-Glu-n-butylamine residue formation under non-reducing and reducing conditions. For b, experiments were run in triplicate, and error bars represent the s.d. Amino acid composition determined after enzymatic hydrolysis of wheat flour (c–e) and gluten (f–h), original and derivatised with mTG alone and with n-butylamine as amine nucleophile under reducing conditions. For (c–h), error bars represent the standard deviation *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001 (n = 3). (i) R5 reactive epitopes’ content (mg of gliadin per kg of product) of wheat flour and gluten, original and derivatised with mTG alone and with n-butylamine as amine nucleophile under reducing conditions after peptic-tryptic digestion. n = 2 different experiments (each with four replicates) and error bars represent the s.d. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001. For sample nomenclature please consult Fig. 6.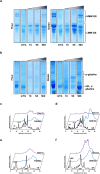

 ) denote 0.5 mg/mL; and filled bars (
) denote 0.5 mg/mL; and filled bars ( ) denote 1.0 mg/mL.
) denote 1.0 mg/mL.
Similar articles
-
Biochemical modifications of gliadins induced by microbial transglutaminase on wheat flour.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1830(11):5166-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.07.021. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23891939
-
Detoxification of Wheat Gluten by Enzymatic Transamidation under Reducing Condition and Its Application in Typical Food Model.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023 Dec;67(23):e2300568. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.202300568. Epub 2023 Oct 22. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2023. PMID: 37867203
-
Prototype Gluten-Free Breads from Processed Durum Wheat: Use of Monovarietal Flours and Implications for Gluten Detoxification Strategies.Nutrients. 2020 Dec 14;12(12):3824. doi: 10.3390/nu12123824. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33327648 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminases: a meeting point for wheat allergy, celiac disease, and food safety.Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005 Dec;37(10):397-403. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16528904 Review.
-
Proteomic analysis in allergy and intolerance to wheat products.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2011 Feb;8(1):95-115. doi: 10.1586/epr.10.98. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21329430 Review.
Cited by
-
Low Gluten Beers Contain Variable Gluten and Immunogenic Epitope Content.Foods. 2023 Aug 29;12(17):3252. doi: 10.3390/foods12173252. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37685187 Free PMC article.
-
The 10,000-Year Success Story of Wheat!Foods. 2021 Sep 8;10(9):2124. doi: 10.3390/foods10092124. Foods. 2021. PMID: 34574233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of Celiac Disease and Other Gluten Related Disorders in Wheat and Strategies for Mitigating Them.Front Nutr. 2020 Feb 7;7:6. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.00006. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32118025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evaluation of part-baked frozen bread produced from wheat flour and guar gum in the diet of celiac patients.J Food Sci Technol. 2021 Jul;58(7):2507-2515. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04757-z. Epub 2020 Sep 2. J Food Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34194087 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Variation of Hazelnut Allergenicity: Is There Any Potential for Selecting Hypoallergenic Varieties?Nutrients. 2020 Jul 16;12(7):2100. doi: 10.3390/nu12072100. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32708541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Di Sabatino A. & Corazza G. R. Coeliac disease. Lancet 373, 1480–1493 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Schuppan D., Junker Y. & Barisani D. Celiac Disease: From Pathogenesis to Novel Therapies. Gastroenterology 137, 1912–1933 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Di Sabatino A. et al. The function of tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 11, 746–753 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Zannini E., Kingston W., Arendt E. K. & Waters D. M. Technological challenges and strategies for developing low-protein/protein-free cereal foods for specific dietary management. Food Res. Int. 54, 935–950 (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

