Efficacy and Safety Study of Olmesartan Medoxomil, Amlodipine, and Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy in Patients with Hypertension Not Controlled with Olmesartan Medoxomil and Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter Trial
- PMID: 26691333
- PMCID: PMC4819539
- DOI: 10.1007/s40256-015-0156-x
Efficacy and Safety Study of Olmesartan Medoxomil, Amlodipine, and Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy in Patients with Hypertension Not Controlled with Olmesartan Medoxomil and Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter Trial
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Efficacy and Safety Study of Olmesartan Medoxomil, Amlodipine, and Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy in Patients with Hypertension Not Controlled with Olmesartan Medoxomil and Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter Trial.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2016 Apr;16(2):139. doi: 10.1007/s40256-016-0167-2. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26994003 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: This study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of triple fixed-dose combination (FDC) therapy with olmesartan medoxomil (OM) 20 mg, amlodipine (AML) 5 mg, and hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 12.5 mg (OM/AML/HCTZ 20/5/12.5) in Korean patients with moderate hypertension not controlled with dual FDC therapy (OM/HCTZ 20/12.5).
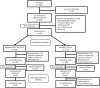
Methods: In this multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group study, Korean patients aged 20 to 75 years with stage 2 hypertension who had a mean seated diastolic blood pressure (msDBP) ≥100 mmHg were enrolled when their BP was uncontrolled [mean seated systolic BP (msSBP)/msDBP >140/90 mmHg or msSBP/msDBP >130/80 mmHg with diabetes or chronic kidney disease] with 4-week dual FDC therapy (OM/HCTZ 20/12.5). The patients were randomized to receive either OM/AML/HCTZ 20/5/12.5 or OM/HCTZ 20/12.5 once daily for 8 weeks. At the end of 8 weeks, patients with uncontrolled BP were assigned to receive either OM/AML/HCTZ 40/5/12.5 or OM/AML/HCTZ 20/5/12.5 in an additional 8-week open-label extension period.
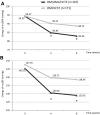
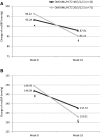
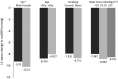
Results: A total of 623 patients received a 4-week run-in treatment with OM/HCTZ, 341 patients were randomized, and finally, 167 patients in the OM/AML/HCTZ group and 171 patients in the OM/HCTZ group were analyzed for the full analysis set. Non-responders after the 8 weeks of double-blind treatment continued the 8-week open-label treatment with OM/AML/HCTZ 40/5/12.5 mg (n = 32) or OM/AML/HCTZ 20/5/12.5 mg (n = 71). After 8 weeks of double-blind treatment, the changes in msDBP were -9.50 (8.46) mmHg in the OM/AML/HCTZ group and -4.23 (7.41) mmHg in the OM/HCTZ group (both p < 0.0001 vs. baseline; p < 0.0001 between groups). The response rates for both msSBP and msDBP at week 8 were 65.27 % in the OM/AML/HCTZ group and 37.43 % in the OM/HCTZ group (p < 0.0001 between groups). The response rates for both msSBP and msDBP at week 16 after open-label treatment were 18.75 % in the OM/AML/HCTZ 40/5/12.5 group and 46.48 % in the OM/AML/HCTZ 20/5/12.5 group (p = 0.0073 between groups). All medications were well tolerated.
Conclusion: In Korean patients with moderate hypertension not controlled with dual FDC therapy (OM/HCTZ 20/12.5) as first-line therapy, switching to triple FDC therapy (OM/AML/HCTZ 20/5/12.5) was associated with significant BP reductions and greater achievement of BP goals, and was well tolerated (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01838850).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triple therapy with olmesartan medoxomil, amlodipine besylate, and hydrochlorothiazide in adult patients with hypertension: The TRINITY multicenter, randomized, double-blind, 12-week, parallel-group study.Clin Ther. 2010 Jul;32(7):1252-69. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2010.07.008. Clin Ther. 2010. PMID: 20678674 Clinical Trial.
-
Triple-Combination therapy with olmesartan, amlodipine, and hydrochlorothiazide in black and non-black study participants with hypertension: the TRINITY randomized, double-blind, 12-week, parallel-group study.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012 Aug 1;12(4):233-43. doi: 10.1007/BF03261832. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2012. PMID: 22799613 Clinical Trial.
-
Olmesartan/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide in participants with hypertension and diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or chronic cardiovascular disease: a subanalysis of the multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group TRINITY study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012 Oct 30;11:134. doi: 10.1186/1475-2840-11-134. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2012. PMID: 23110471 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide: fixed-dose combination in hypertension.Drugs. 2011 Jan 22;71(2):209-20. doi: 10.2165/11206770-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21275446 Review.
-
Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan medoxomil or valsartan in combination with amlodipine: a review of factorial-design studies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Jan;25(1):177-85. doi: 10.1185/03007990802597456. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19210150 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Pill Combination with Three Antihypertensive Agents to Improve Blood Pressure Control in Hypertension: Focus on Olmesartan-Based Combinations.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023 Mar;30(2):109-121. doi: 10.1007/s40292-023-00563-8. Epub 2023 Jan 25. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2023. PMID: 36696054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weber MA, Schiffrin EL, White WB, Mann S, Lindholm LH, Kenerson JG, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypertension in the community a statement by the American Society of Hypertension and the International Society of Hypertension. J Hypertens. 2014;32(1):3–15. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000065. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) J Hypertens. 2013;31(7):1281–1357. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000431740.32696.cc. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

