Wnt/β-catenin signaling in kidney injury and repair: a double-edged sword
- PMID: 26692289
- PMCID: PMC4731262
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.153
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in kidney injury and repair: a double-edged sword
Abstract
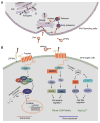
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling cascade is an evolutionarily conserved, highly complex pathway that is known to be involved in kidney injury and repair after a wide variety of insults. Although the kidney displays an impressive ability to repair and recover after injury, these repair mechanisms can be overwhelmed, leading to maladaptive responses and eventual development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Emerging evidence demonstrates that Wnt/β-catenin signaling possesses dual roles in promoting repair/regeneration or facilitating progression to CKD after acute kidney injury (AKI), depending on the magnitude and duration of its activation. In this review, we summarize the expression, intracellular modification, and secretion of Wnt family proteins and their regulation in a variety of kidney diseases. We also explore our current understanding of the potential mechanisms by which transient Wnt/β-catenin activation positively regulates adaptive responses of the kidney after AKI, and discuss how sustained activation of this signaling triggers maladaptive responses and causes destructive outcomes. A better understanding of these mechanisms may offer important opportunities for designing targeted therapy to promote adaptive kidney repair/recovery and prevent progression to CKD in patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

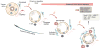
Similar articles
-
[Wnt/β-catenin signaling in kidney repair and fibrosis after injury].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 25;74(1):15-27. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35199122 Chinese.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor protects against acute kidney injury via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022 Jun 1;322(6):F611-F624. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00023.2022. Epub 2022 Apr 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35403451
-
Sustained Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Drives AKI to CKD Progression.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jun;27(6):1727-40. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015040449. Epub 2015 Oct 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26453613 Free PMC article.
-
The WNT/β-catenin system in chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorder syndrome.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Oct;55(10):2527-2538. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03569-2. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36964322 Review.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin in Acute Kidney Injury and Progression to Chronic Kidney Disease.Semin Nephrol. 2020 Mar;40(2):126-137. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2020.01.004. Semin Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32303276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Krüppel-like factor 4 modulates the miR-101/COL10A1 axis to inhibit renal fibrosis after AKI by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2316259. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2316259. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38345033 Free PMC article.
-
Nephronophthisis-Pathobiology and Molecular Pathogenesis of a Rare Kidney Genetic Disease.Genes (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;12(11):1762. doi: 10.3390/genes12111762. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt Signaling in Kidney Development and Disease.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018 Jan;153:181-207. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.11.019. Epub 2017 Dec 30. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018. PMID: 29389516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activated renal tubular Wnt/β-catenin signaling triggers renal inflammation during overload proteinuria.Kidney Int. 2018 Jun;93(6):1367-1383. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2017.12.017. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Kidney Int. 2018. PMID: 29605095 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 16;12:719880. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.719880. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34483931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berger K, Moeller MJ. Mechanisms of epithelial repair and regeneration after acute kidney injury. Semin Nephrol. 2014;34:394–403. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida M, Honma S. Regeneration of injured renal tubules. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;124:117–122. - PubMed
-
- Sharfuddin AA, Molitoris BA. Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7:189–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

