Symptom burden, Metabolic profile, Ultrasound findings, Rhythm, neurohormonal activation, haemodynamics and health-related quality of life in patients with atrial Fibrillation (SMURF): a protocol for an observational study with a randomised interventional component
- PMID: 26692555
- PMCID: PMC4691757
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008723
Symptom burden, Metabolic profile, Ultrasound findings, Rhythm, neurohormonal activation, haemodynamics and health-related quality of life in patients with atrial Fibrillation (SMURF): a protocol for an observational study with a randomised interventional component
Abstract
Introduction: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia, with an estimated prevalence of 1.5-2%. It is an independent risk factor for ischaemic stroke and is estimated to cause about 20-25% of all stroke cases. AF has a great impact on health-related quality of life (HRQoL); however, one unresolved issue related to AF is the wide variation in its symptoms.
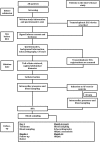
Methods and analysis: The symptom burden, metabolic profile, ultrasound findings, rhythm, neurohormonal activation, haemodynamics and HRQoL in patients with AF (Symptom burden, Metabolic profile, Ultrasound findings, Rhythm, neurohormonal activation, haemodynamics and health-related quality of life in patients with atrial Fibrillation, SMURF) study is a prospective observational, cohort study, with a randomised interventional part. The aim of the study is to investigate, in patients with AF, the relationship between symptom burden and metabolic aspects, atrial function and different neurohormones, and the effect of radiofrequency ablation (RFA). The interventional part of the study will give an insight into the neurohormonal and intracardiac pressure changes directly after initiation of AF. Consecutive patients with symptomatic AF accepted for treatment with RFA for the first time at Linköping University Hospital are eligible for participation. The enrolment started in January 2012, and a total of 200 patients are to be included into the study, with 45 of them being enrolled into the interventional study with initiation of AF. The sample size of the interventional study is based on a small pilot study with 5 patients induced to AF while 2 served as controls. The results indicated that, in order to find a statistically significant difference, there was a need to include 28 patients; for safety reasons, 45 patients will be included.
Ethics and dissemination: The SMURF study is approved by the Regional Ethical Review Board at the Faculty of Health Sciences, Linköping, Sweden. The results will be presented through peer-review journals and conference presentation.
Trial registration number: NCT01553045; Pre-results.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation for patients with atrial fibrillation receiving catheter ablation: protocol for a feasibility randomised controlled trial (RCT) with embedded process evaluation.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 30;15(1):e088460. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-088460. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39890138 Free PMC article.
-
Curative catheter ablation in atrial fibrillation and typical atrial flutter: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Nov;12(34):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-198. doi: 10.3310/hta12340. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 19036232
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Haemodynamic changes after atrial fibrillation initiation in patients eligible for catheter ablation: a randomized controlled study.Eur Heart J Open. 2023 Oct 31;3(6):oead112. doi: 10.1093/ehjopen/oead112. eCollection 2023 Nov. Eur Heart J Open. 2023. PMID: 38025650 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of improvement in arrhythmia-specific symptoms and health-related quality of life after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation.Clin Cardiol. 2019 Feb;42(2):247-255. doi: 10.1002/clc.23134. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Clin Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30548275 Free PMC article.
-
The association between alcohol consumption, cardiac biomarkers, left atrial size and re-ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation referred for catheter ablation.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 10;14(4):e0215121. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215121. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30970005 Free PMC article.
-
Neurohormonal Activation After Atrial Fibrillation Initiation in Patients Eligible for Catheter Ablation: A Randomized Controlled Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Dec 12;5(12):e003957. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003957. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27956398 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Echocardiographic and Biochemical Factors Predicting Arrhythmia Recurrence After Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation-An Observational Study.Front Physiol. 2019 Oct 2;10:1215. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01215. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31632285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R et al. . 2012 Focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Eur Heart J 2012;33:2719–47. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs253 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical