Effect of antiretroviral therapy on mucocutaneous manifestations among Human Immunodeficiency Virus-infected patients in a tertiary care centre in South India
- PMID: 26692610
- PMCID: PMC4660558
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7184.167160
Effect of antiretroviral therapy on mucocutaneous manifestations among Human Immunodeficiency Virus-infected patients in a tertiary care centre in South India
Abstract
Background: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infection produces a wide range of infectious and noninfectious dermatoses which correlate with the degree of immunodeficiency. Since the introduction of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), there has been a dramatic decrease in the incidence of HIV-associated dermatoses. However, HAART itself causes various cutaneous adverse drug reactions.
Aims: To assess the various mucocutaneous manifestations in HIV-infected individuals and its association with CD4 count and to assess the effect of HAART on mucocutaneous manifestations.
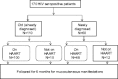
Materials and methods: Of the 170 patients recruited, 110 patients were previously diagnosed with HIV and were on follow-up. The rest 60 patients were newly diagnosed cases at recruitment, and these patients were followed up every month for mucocutaneous manifestations for a period of 6 months.
Results: Of the 170 patients screened, 69.41% patients had at least one mucocutaneous lesion at presentation. Fungal, viral, and bacterial infections were observed present in 17.6%, 10.6%, and 9.4% patients, respectively. There was a significant difference in the occurrence of candidal infections in the HAART versus non-HAART group (P = 0.0002). Candidiasis (P ≤ 0.0001) and human papillomavirus infection (P = 0.0475) occurred more commonly with CD4 count <200 cells/mm (3) . Among the noninfectious dermatoses, inflammatory dermatoses (17.6%) were more commonly observed at recruitment followed by adverse cutaneous drug reactions (16.5%) and neoplasms (5.3%).
Conclusion: HAART has significantly altered the patterns of mucocutaneous manifestations. The prevalence of both infectious and inflammatory dermatoses has come down. However, there is an increase in the incidence of adverse cutaneous drug reactions.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapy; CD4 count; Human Immunodeficiency Virus infection; mucocutaneous manifestations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of antiretroviral therapies in mucocutaneous manifestations in HIV-infected children over a period of two decades.Br J Dermatol. 2005 Aug;153(2):382-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06758.x. Br J Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 16086754
-
Mucocutaneous manifestations of HIV-infected patients in the era of HAART in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013 Mar;27(3):376-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04429.x. Epub 2012 Jan 3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013. PMID: 22212015
-
Correlating CD4 count with mucocutaneous manifestations in HIV-positive patients: A prospective study.Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2017 Jul-Dec;38(2):128-135. doi: 10.4103/ijstd.IJSTD_130_15. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2017. PMID: 30148265 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the impact of HIV genotypic drug resistance testing on therapy efficacy.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001;63(5):447-73. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2001. PMID: 11813503 Review.
-
Prevalence of HIV-related oral manifestations and their association with HAART and CD4+ T cell count: a review.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2018 Jan-Feb;32(2 Suppl. 1):51-59. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2018. PMID: 29460518 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of dermatological manifestations with CD4 count among people living with HIV attending tertiary care hospital of South Gujarat.Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2023 Jul-Dec;44(2):147-151. doi: 10.4103/ijstd.ijstd_24_23. Epub 2023 Dec 6. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2023. PMID: 38223138 Free PMC article.
-
Mucocutaneous Manifestations Among HIV-Infected Patients in Madagascar: Cross-Sectional Study.JMIR Dermatol. 2023 Aug 15;6:e47199. doi: 10.2196/47199. JMIR Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37581910 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of sexually transmitted infection among HIV patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy attending a tertiary care center in western Rajasthan.Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2025 Jan-Jun;46(1):92-93. doi: 10.4103/ijstd.ijstd_21_24. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 2025. PMID: 40546385 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dermatological Manifestations of HIV/AIDS Individuals in Shiraz, South of Iran.J Glob Infect Dis. 2018 Apr-Jun;10(2):80-83. doi: 10.4103/0974-777X.233000. J Glob Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29910568 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence and spectrum of mucocutaneous disease in South African people living with HIV and accessing care at a district-level hospital.South Afr J HIV Med. 2020 Dec 10;21(1):1154. doi: 10.4102/sajhivmed.v21i1.1154. eCollection 2020. South Afr J HIV Med. 2020. PMID: 33354365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han J, Lun WH, Meng ZH, Huang K, Mao Y, Zhu W, et al. Mucocutaneous manifestations of HIV-infected patients in the era of HAART in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:376–82. - PubMed
-
- Huang XJ, Li HY, Chen DX, Wang XC, Li ZC, Wu YS, et al. Clinical analysis of skin lesions in 796 Chinese HIV- positive patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:552–6. - PubMed
-
- Shobhana A, Guha SK, Neogi DK. Mucocutaneous manifestations of HIV infection. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2004;70:82–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

