Cataract Surgery Audit at a Private Hospital in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 26692725
- PMCID: PMC4660540
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-9233.167820
Cataract Surgery Audit at a Private Hospital in Saudi Arabia
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Cataract Surgery Audit at a Private Hospital in Saudi Arabia.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct-Dec;23(4):333. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.194126. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27994403 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: To assess the visual outcomes following cataract surgeries at a Private Eye Hospital in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Methods: This was a cohort study of cataract surgeries performed from January to June 2014. Preoperative data were collected on patient demographics presenting and best corrected distance visual acuity (BCVA) and ocular comorbidity. Data were also collected on the type of surgery, type of intraocular lens (IOLs) implanted, and complications. BCVA and refractive status at 6-8 weeks postoperatively were noted. The predictors of vision ≥ 6/18 were identified.
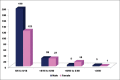
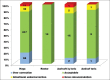
Results: Four hundred eyes of 400 patients underwent cataract surgery. There were 235 (59%) males. Presenting preoperative vision was < 6/60 in 52 (13%) eyes. There were 395 (99%) eyes that underwent IOL implantation following phacoemulsification and 4 eyes received a sulcus fixated IOL. A single piece aspheric IOL was implanted in 358 (90%) eyes and a toric IOL was implanted in 31 (8%) eyes. Postoperative BCVA was classified as a "good outcome" (≥ 6/18) in 320 (80%) and a "poor outcome" (< 6/60) in 24 (6%) eyes. Young age (adjusted odds ratio (OR) = 0.97, P = 0.01), male (adjusted OR = 2.4, P = 0.002), and ocular co-morbidities (adjusted OR = 0.2, P < 0.001) were predictors of vision ≥ 6/18. Complications included a dropped nucleus and a posterior capsular tear in 2 eyes each. Two hundred and fifty-two (63%) eyes were emmetropic or intentionally myopic for distance. Astigmatism < 2 D was present in 264 (66%) eyes and astigmatism > 2 D was present in 33 (8%) eyes.
Conclusion: The recent trend of intentional overcorrection in one eye following modern cataract surgery in order to provide some functional near vision indicates that benchmark for success in getting "good visual outcomes" postoperatively (vision of ≥ 6/18) may need to be revised.
Keywords: Cataract; Intraocular Lens Implant; Surgical Audit; Visual Acuity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rotational performance and corneal astigmatism correction during cataract surgery: aspheric toric intraocular lens versus aspheric nontoric intraocular lens with opposite clear corneal incision.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014 Aug;40(8):1355-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2013.11.039. Epub 2014 Jul 1. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2014. PMID: 24996893 Clinical Trial.
-
Toric vs aspherical control intraocular lenses in patients with cataract and corneal astigmatism: a randomized clinical trial.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014 Dec;132(12):1462-8. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2014.3602. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 25256624 Clinical Trial.
-
[Visual quality comparison after multifocal toric intraocular lens or monofocal toric intraocular lens implantation].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Apr 11;53(4):274-280. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2017.04.009. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28412800 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[THE GUT FEELING OF THE EYES: GUT-EYE AXIS].Harefuah. 2020 Jun;159(6):455-457. Harefuah. 2020. PMID: 32583651 Review. Hebrew.
-
Vision while the eyes move: Getting the full picture.Sci Adv. 2021 Jul 23;7(30):eabk0043. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abk0043. Print 2021 Jul. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34301609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between changes in intraocular pressure and refractive error indices post Cataract Surgery.Pak J Med Sci. 2020 Mar-Apr;36(3):574-577. doi: 10.12669/pjms.36.3.1597. Pak J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32292474 Free PMC article.
-
The Value of Auditing Surgical Records in a Tertiary Hospital Setting.Cureus. 2022 Jan 10;14(1):e21066. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21066. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35155026 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Healthcare Privatization on Access to Surgical Care: Cholecystectomy as a Model.World J Surg. 2017 Feb;41(2):394-401. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3739-z. World J Surg. 2017. PMID: 27734081
-
Erratum: Cataract Surgery Audit at a Private Hospital in Saudi Arabia.Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct-Dec;23(4):333. doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.194126. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27994403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bourne RR, Stevens GA, White RA, Smith JL, Flaxman SR, Price H, et al. Causes of vision loss Worldwide, 1990-2010: A systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2013;1:e339–49. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Cataract in Global Initiative for the Elimination of Avoidable Blindness Action Plan 2006-2011. [Last accessed on 2014 Sep 09]. Available from: http://www.iapb.org/sites/iapb.org/files/6_VISION%202020%20Action%20Plan... .
-
- Gogate P, Vakil V, Khandekar R, Deshpande M, Limburg H. Monitoring and modernization to improve visual outcomes of cataract surgery in a community eye care center in western India. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37:328–34. - PubMed
-
- Hajar S. Cataract Surgery audit in Saudi Arabia. Prevention of Blindness Meeting, Ministry of Health, Saudi Arabia; February. 2014
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources