Bioactive compounds from Carissa opaca roots and xanthine oxidase and alpha-amylase inhibitory activities of their methanolic extract and its fractions in different solvents
- PMID: 26692741
- PMCID: PMC4660506
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-8490.158440
Bioactive compounds from Carissa opaca roots and xanthine oxidase and alpha-amylase inhibitory activities of their methanolic extract and its fractions in different solvents
Abstract
Background: Carissa opaca is known for its many ethnomedicinal uses. There was a need to study its bioactivities and identify its phytochemicals.
Objective: The objective was to isolate and identify phytochemicals from roots of C. opaca and to evaluate xanthine oxidase (XO) and alpha-amylase inhibitory activities of their methanolic extract and its fractions.
Materials and methods: Methanolic extract of finely divided powder of roots of C. opaca was obtained by cold maceration, followed by its fractionation to obtain hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, n-butanolic, and aqueous fractions. Phytochemicals screening was done by standard protocols. XO and alpha-amylase inhibitory activities of the methanolic extract and its fractions were studied. The most active ethyl acetate fraction was subjected to the column and thin layer chromatography to isolate its compounds, which were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography comparison.
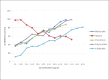
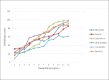
Results: Methanolic extract displayed significant activity against both the enzymes with IC50 of 156.0 mg/mL and 5.6 mg/mL for XO and alpha-amylase, respectively. Ethyl acetate fraction showed highest activity against both the enzymes with IC50 of 129 mg/mL and 4.9 mg/mL for XO and alpha-amylase, respectively. Chloroform fraction had IC50 of 154.2 mg/mL and 5.5 mg/mL for XO and alpha-amylase, respectively. Aqueous fraction exhibited significant efficacy against alpha-amylase (IC50 5.0 mg/mL). Hexane fraction showed good activity against alpha-amylase in a dose-dependent manner but exhibited opposite trend against XO. The compounds isolated from ethyl acetate fraction included limonene, vanillin, lupeol, rutin, quercetin, b-sitosterol, Vitamin E, 2-hydroxyacetophenone, naphthalenone, 2,3,3-trimethyl-2-(3-methylbuta-1,3-dienyl)-6-methylenecyclohexanone, and 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, mono(2-ethylhexyl) ester.
Conclusions: Moderately polar phytochemicals of C. opaca roots possess exploitable inhibitory activity against both the enzymes.
Keywords: Alpha-amylase; Carissa opaca roots; Inhibitory activity; Phytochemicals; Xanthine oxidase.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activities of Carissa opaca Stapf ex Haines Roots Extracts and Their Phytochemical Analysis.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Oct;13(Suppl 3):S544-S548. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_561_16. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 29142412 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents, and the Anti-Oxidative Potential and Lipid Peroxidation Inhibitory Activity of Methanolic Extract of Carissa opaca Roots and Its Fractions in Different Solvents.Antioxidants (Basel). 2014 Oct 20;3(4):671-83. doi: 10.3390/antiox3040671. Antioxidants (Basel). 2014. PMID: 26785233 Free PMC article.
-
Study of phenolic content and urease and alpha-amylase inhibitory activities of methanolic extract of Rumex acetosella roots and its sub-fractions in different solvents.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2013 May;26(3):553-9. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2013. PMID: 23625429
-
Study of alpha-amylase and urease inhibitory activities of Melilotus indicus (Linn.) All.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014 Jan;27(1):57-61. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 24374453
-
A Review on the Pharmacological Activities and Phytochemicals of Alpinia officinarum (Galangal) Extracts Derived from Bioassay-Guided Fractionation and Isolation.Pharmacogn Rev. 2017 Jan-Jun;11(21):43-56. doi: 10.4103/phrev.phrev_55_16. Pharmacogn Rev. 2017. PMID: 28503054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Antidiabetic, Anti-Obesity and Antioxidant Analysis of Ocimum basilicum Aerial Biomass and in Silico Molecular Docking Simulations with Alpha-Amylase and Lipase Enzymes.Biology (Basel). 2019 Dec 4;8(4):92. doi: 10.3390/biology8040092. Biology (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817095 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Antiasthmatic Activity of Carissa opaca in Animal Models.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Sep 6;2022:7011789. doi: 10.1155/2022/7011789. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 38533238 Free PMC article.
-
The Genus Carissa: An Ethnopharmacological, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2017 Apr;7(2):181-199. doi: 10.1007/s13659-017-0123-0. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2017. PMID: 28243901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activities of Carissa opaca Stapf ex Haines Roots Extracts and Their Phytochemical Analysis.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Oct;13(Suppl 3):S544-S548. doi: 10.4103/pm.pm_561_16. Epub 2017 Oct 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 29142412 Free PMC article.
-
Extracts, Fractions, and Subfractions from Purple-Orange Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.): Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Potential and Antioxidant Properties.Molecules. 2025 Jun 3;30(11):2442. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112442. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40509329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin CM, Chen CS, Chen CT, Liang YC, Lin JK. Molecular modeling of flavonoids that inhibits xanthine oxidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;294:167–72. - PubMed
-
- Apaya KL, Chichioco-Hernandez CL. Xanthine oxidase inhibition of selected Philippine medicinal plants. J Med Plants Res. 2011;5:289–92.
-
- Fagugli RM, Gentile G, Ferrara G, Brugnano R. Acute renal and hepatic failure associated with allopurinol treatment. Clin Nephrol. 2008;70:523–6. - PubMed
-
- Hara Y, Honda M. The inhibition of α-amylase by tea catechins. Agric Biol Chem. 1990;54:1939–45.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
