Alpha-amylase inhibitory activity and sterol composition of the marine algae, Sargassum glaucescens
- PMID: 26692744
- PMCID: PMC4660509
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-8490.167893
Alpha-amylase inhibitory activity and sterol composition of the marine algae, Sargassum glaucescens
Abstract
Background: Sargassum species (phaeophyceae) are economically important brown algae in southern parts of Iran. Sargassum is mainly harvested as a row material in alginate production industries and is a source of plant foods or plant bio-stimulants even a component of animal foods.
Objective: In this study, Sargassum glaucescens, collected from the seashore of Chabahar, was employed for phytochemical and biological evaluations.
Materials and methods: For that purpose, the dried algae was extracted by methanol and subjected to different chromatographic separation methods.
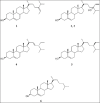
Results: Six sterols, fucosterol (1), 24(S)-hydroxy-24-vinylcholesterol (2), 24(R)-hydroxy-24-vinylcholesterol (3), stigmasterol (4), β-sitosterol (5) and cholesterol (6) were identified by spectroscopic methods including (1)H-NMR, (13)C-NMR and mass spectroscopy. In vitro alpha-amylase inhibitory test was performed on the methanolic extract and the results revealed a potent inhibition (IC50 = 8.9 ± 2.4 mg/mL) of the enzyme compared to acarbose as a positive control.
Conclusion: Various biological activities and distribution of sterols in Sargassum genus have been critically reviewed here. The results concluded that these algae are a good candidate for further anti-diabetic investigations in animals and human.
Keywords: Alpha-amylase inhibitor; Brown algae; Sargassum glaucescens; Sterol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
24(R, S)-Saringosterol - From artefact to a biological medical agent.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Sep;212:105942. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105942. Epub 2021 Jun 16. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34144153
-
Sterols from Sargassum oligocystum, a brown algae from the Persian Gulf, and their bioactivity.Nat Prod Res. 2012;26(8):774-7. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2010.548812. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Nat Prod Res. 2012. PMID: 21895454
-
A cytotoxic hydroperoxy sterol from the brown alga, Nizamuddinia zanardinii.Daru. 2013 Mar 18;21(1):24. doi: 10.1186/2008-2231-21-24. Daru. 2013. PMID: 23497504 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and natural products diversity of the brown algae genus Sargassum.RSC Adv. 2020 Jul 1;10(42):24951-24972. doi: 10.1039/d0ra03576a. eCollection 2020 Jun 29. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35517468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fucosterol of Marine Macroalgae: Bioactivity, Safety and Toxicity on Organism.Mar Drugs. 2021 Sep 27;19(10):545. doi: 10.3390/md19100545. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34677444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The inhibitory effect of some natural bioactive compounds against SARS-CoV-2 main protease: insights from molecular docking analysis and molecular dynamic simulation.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2020;55(11):1373-1386. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2020.1826192. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2020. PMID: 32998618 Free PMC article.
-
α-Amylase and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitory effects of Melicope latifolia bark extracts and identification of bioactive constituents using in vitro and in silico approaches.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):964-973. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1948065. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34347568 Free PMC article.
-
Antihyperglycemic and anti-type 2 diabetic activity of marine hydroquinone isolated from brown algae (Dictyopteris polypodioides).J Tradit Complement Med. 2023 Mar 20;13(4):408-416. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2023.03.007. eCollection 2023 Jul. J Tradit Complement Med. 2023. PMID: 37396160 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Anti-Oxidant, In Vivo Anti-Hyperglycemic, and Untargeted Metabolomics-Aided-In Silico Screening of Macroalgae Lipophilic Extracts for Anti-Diabetes Mellitus and Anti-COVID-19 Potential Metabolites.Metabolites. 2023 Nov 27;13(12):1177. doi: 10.3390/metabo13121177. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38132859 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of Green Seaweed Halimeda tuna Extract from the Coast of Lhok Bubon, Aceh.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 14;12(2):393. doi: 10.3390/plants12020393. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36679105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hogan MC. Brown algae. In: Monosson E, Cleveland CJ, editors. Encyclopedia of Earth. Washington, DC: National Council for Science and the Environment; 2011.
-
- Boaden PJ. The adventives seaweed Sargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt in Sterangford Lough, Northen Ireland. Ir Nat J. 1995;25:111–3.
-
- Cannel RJ. Algae as a source of biologically active products. Pestic Sci. 2006;39:143–53.
-
- Xu FQ, Feng YY, Guo L, Guo GL, Yan BL. On chemical constitutes from Sargassum pallidum. Anhui Nongye Kexue. 2013;41:6658–9.
-
- Liu X, Wang CY, Shao CL, Wei YX, Wang BG, Sun LL, et al. Chemical constituents from Sargassum pallidum (Turn). C. Agardh Biochem Syst Ecol. 2009;37:127–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources