Hemostasis Achieved Endoscopically for Diverticular Bleeding from the Horizontal Portion of the Duodenum
- PMID: 26692767
- PMCID: PMC4671547
- DOI: 10.4137/CGast.S32421
Hemostasis Achieved Endoscopically for Diverticular Bleeding from the Horizontal Portion of the Duodenum
Abstract
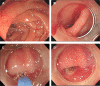
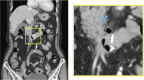
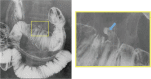
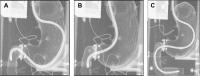
Diverticulum of the horizontal portion of the duodenum is a rare cause of upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. Since it is difficult to access the horizontal portion of the duodenum by standard upper GI endoscopy, only a very few cases of endoscopic hemostasis have been reported. Herein, we report a case of diverticular bleeding from the horizontal portion of the duodenum for which hemostasis was achieved using a small-caliber colonoscope, which has an insertion part designed with a passive-bending function/high-force transmission and a transparent tip hood.
Keywords: diverticular bleeding; duodenum; endoscopic hemostasis; passive-bending function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hemostasis achieved endoscopically for duodenal diverticular bleeding by removing a large blood clot using a snare.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug;13(4):615-620. doi: 10.1007/s12328-020-01100-z. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32052269
-
Endoscopic management of duodenal diverticular bleeding.Gastrointest Endosc. 2007 Nov;66(5):1042-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.07.014. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007. PMID: 17963893
-
Extravasation and fluid collection on computed tomography imaging in patients with colonic diverticular bleeding.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 9;15(4):e0229884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229884. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32271779 Free PMC article.
-
[Endoscopy, angiography, surgery: diagnostic and therapeutic algorithms for diverticular bleeding].Chirurg. 2019 Aug;90(8):621-630. doi: 10.1007/s00104-019-0950-0. Chirurg. 2019. PMID: 30976892 Review. German.
-
Endoscopic management of colonic diverticular bleeding.Dig Endosc. 2015 Nov;27(7):720-5. doi: 10.1111/den.12534. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Dig Endosc. 2015. PMID: 26258405 Review.
Cited by
-
Duodenal Diverticular Bleeding Treated with Endoscopy or Transcatheter Arterial Embolization: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review.Intern Med. 2023 Dec 15;62(24):3565-3569. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1742-23. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37081681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perforated Duodenal Diverticulum With Postoperative Diverticulum Bleeding Successfully Treated Using Transcatheter Arterial Embolization.Cureus. 2021 Sep 23;13(9):e18219. doi: 10.7759/cureus.18219. eCollection 2021 Sep. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34722030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen YY, Yen HH, Soon MS. Impact of endoscopy in the management of duodenal diverticular bleeding: experience of a single medical center and a review of recent literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007;66:831–835. - PubMed
-
- Afridi SA, Fichtenbaum CJ, Taubin H. Review of duodenal diverticula. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991;86:935–938. - PubMed
-
- Yin WY, Chen HT, Huang SM, Lin HH, Chang TM. Clinical analysis and literature review of massive duodenal diverticular bleeding. World J Surg. 2001;25:848–855. - PubMed
-
- Mathis KL, Farley DR. Operative management of symptomatic duodenal diverticula. Am J Surg. 2007;193:305–308. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

