IKK phosphorylation of NF-κB at serine 536 contributes to acquired cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell cancer
- PMID: 26693062
- PMCID: PMC4656733
IKK phosphorylation of NF-κB at serine 536 contributes to acquired cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell cancer
Abstract
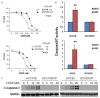
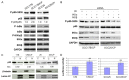
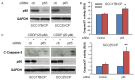
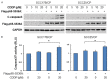
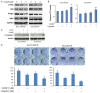
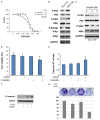
Current treatment methods for advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) include surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. For recurrent and metastatic HNSCC, cisplatin is the most common treatment option, but most of patients will eventually develop cisplatin resistance. Therefore, it is imperative to define the mechanisms involved in cisplatin resistance and find novel therapeutic strategies to overcome this deadly disease. In order to determine the role of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in contributing to acquired cisplatin resistance in HNSCC, the expression and activity of NF-κB and its upstream kinases, IKKα and IKKβ, were evaluated and compared in three pairs of cisplatin sensitive and resistant HNSCC cell lines, including a pair of patient derived HNSCC cell line. The experiments revealed that NF-κB p65 activity was elevated in cisplatin resistant HNSCC cells compared to that in their parent cells. Importantly, the phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 at serine 536 and the phosphorylation of IKKα and IKKβ at their activation loops were dramatically elevated in the resistant cell lines. Furthermore, knockdown of NF-κB or overexpression of p65-S536 alanine (p65-S536A) mutant sensitizes resistant cells to cisplatin. Additionally, the novel IKKβ inhibitor CmpdA has been shown to consistently block the phosphorylation of NF-κB at serine 536 while also dramatically improving the efficacy of cisplatin in inhibition of cell proliferation and induction of apoptosis in the cisplatin resistant cancer cells. These results indicated that IKK/NF-κB plays a pivotal role in controlling acquired cisplatin resistance and that targeting the IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway may provide a possible therapeutic method to overcome the acquired resistance to cisplatin in HNSCC.
Keywords: HNSCC; IKK; IKKβ inhibitors; NF-κB; cisplatin resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of migration, invasion, and metastasis of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through IKKβ inhibition.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020 Apr;37(2):283-292. doi: 10.1007/s10585-020-10021-7. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020. PMID: 32020377 Free PMC article.
-
A positive feedback loop involving EGFR/Akt/mTORC1 and IKK/NF-kB regulates head and neck squamous cell carcinoma proliferation.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):31892-906. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7441. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26895469 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IKKβ/NF-κB signaling pathway to improve Dasatinib efficacy in suppression of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Discov. 2020 May 15;6:36. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-0270-7. eCollection 2020. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 32435511 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837071 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory related gene IKKα, IKKβ, IKKγ cooperates to determine liver cancer stem cells progression by altering telomere via heterochromatin protein 1-HOTAIR axis.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):50131-50149. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10321. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27367027 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of migration, invasion, and metastasis of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through IKKβ inhibition.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020 Apr;37(2):283-292. doi: 10.1007/s10585-020-10021-7. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020. PMID: 32020377 Free PMC article.
-
A1CF Binding to the p65 Interaction Site on NKRF Decreased IFN-β Expression and p65 Phosphorylation (Ser536) in Renal Carcinoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 22;25(7):3576. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073576. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612387 Free PMC article.
-
Morin decreases galectin-3 expression and sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2018 Dec;298(6):1181-1194. doi: 10.1007/s00404-018-4912-4. Epub 2018 Sep 28. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2018. PMID: 30267152 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by the SRC/ETS-1 signaling pathway.BMC Cancer. 2019 May 22;19(1):485. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5664-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31118072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Pignon JP, le Maitre A, Maillard E, Bourhis J MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-analysis of chemo-therapy in head and neck cancer (MACH-NC): an update on 93 randomised trials and 17,346 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Molin Y, Fayette J. Current chemotherapies for recurrent/metastatic head and neckcancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2011;22:621–625. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
