The Orthodontic Management of an Adult with Sickle Cell Disease
- PMID: 26693198
- PMCID: PMC4676597
- DOI: 10.4314/gmj.v49i3.13
The Orthodontic Management of an Adult with Sickle Cell Disease
Abstract
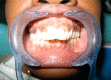
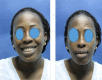
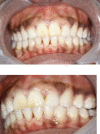
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a hereditary blood disorder characterized by abnormally shaped red cells. SCD frequently exhibits multisystemic manifestations including oral and craniofacial disorders. Craniofacial features such as maxillary protrusion and more forward growth of the mandible with significantly retruded maxillary and mandibular incisors are common. When a patient with Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) needs orthodontic treatment, it is important for the practitioner involved to know about the disease and the respective treatment because of the importance of complete blood supply after application of intraoral and extraoral forces. This article describes a sickle cell HbSS patient with orthodontic problems and how she was successfully managed at the University of Ghana Dental School.
Keywords: craniofacial features; gnatopathy; orthodontic treatment; sickle cell disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ohene-frempong K, Oduro J, Tetteh H, Nkrumah F. Screening newborns for sickle cell disease in Ghana. Pediatrics. 2008;121(suppl 2):120–121.
-
- Konotey-Ahulu FID. The sickle cell disease patient. Tetteh-A'domeno Publishing Company; 1991. pp. 178–188.
-
- Franco BM, Goncalves JCH, dos Santos CRR. Buccal manifestations of sickle cell anemia and their implications in the dentistry services. Arq Odontol. 2007:92–96.
-
- Alves PV, Alves DK, de Souza MM, Torres SR. orthodontic treatment of patients with sickle cell anemia. Angle orthod. 2006;76:269–273. - PubMed
-
- Kelleher M, Bishop K, Briggs P. oral complications associated with sickle cell anemia: a review and case report. Oral surg oral med oral pathol oral radiol endod. 1996;82:225–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical