Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of Scutellaria luteo-coerulea Bornm. & Sint. on leukemia cancer cell lines K562 and HL-60
- PMID: 26693412
- PMCID: PMC4678500
Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of Scutellaria luteo-coerulea Bornm. & Sint. on leukemia cancer cell lines K562 and HL-60
Abstract
Objective: Scutellaria (Lamiaceae) has been implicated for medicinal purposes both in modern and traditional medicine. Some species of the genus Scutellaria has extensively been studied for anticancer activity. Scutellaria luteo-coerulea (S. luteo-coerulea) is one of the Iranian species of the genus Scutellaria.
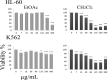
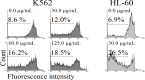
Materials and methods: In the present study, cytotoxic and apoptogenic properties of CH2Cl2, EtOAc, n-BuOH, and H2O fractions of S. luteo-coerulea were investigated on K562. Moreover, HL-60. DNA fragmentation in apoptotic cells were determined by propidium iodide (PI) staining (sub-G1 peak).
Results: Scutellaria luteo-coerulea inhibited the growth of malignant cells in a dose-dependent manner. Among solvent fractions of S. luteo-coerulea, the CH2Cl2 fraction was found to be the most cytotoxic one among others. Sub-G1 peak in flow cytometry histogram of treated cells suggested the induction of apoptosis in S. luteo-coerulea.
Conclusion: Scutellaria luteo-coerulea could be a novel candidate for further analytical elucidation in respect to fine major components responsible for the cytotoxic effect of the plant also clinical evaluations.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cytotoxicity; Lamiaceae; Scutellaria; luteo-coerulea.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction by Scutellaria pinnatifida A. Ham. on HL-60 and K562 leukemic cell lines.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;39(1):307-12. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 16. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25546119
-
Analyzing Cytotoxic and Apoptogenic Properties of Scutellaria litwinowii Root Extract on Cancer Cell Lines.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:160682. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nep214. Epub 2011 Mar 9. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 20028719 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellaria litwinowii induces apoptosis through both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways in human promyelocytic leukemia cells.Nutr Cancer. 2012;64(1):80-8. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2012.630162. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Nutr Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22098153
-
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. (Lamiaceae): a review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019 Sep;71(9):1353-1369. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13129. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31236960 Review.
-
Scutellaria: Debates on the anticancer property.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Sep;105:1299-1310. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.107. Epub 2018 Jun 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30021367 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Biebersteinia multifida hydro-ethanol extract on proliferation and apoptosis of human prostate cancer and human embryonic kidney cells.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2016 Nov-Dec;6(6):671-677. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2016. PMID: 28078247 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Proliferative Effect of Wogonin on Ovary Cancer Cells Involves Activation of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Nov 10;25:8465-8471. doi: 10.12659/MSM.917823. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31707402 Free PMC article.
-
A study on the modulation of alpha-synuclein fibrillation by Scutellaria pinnatifida extracts and its neuroprotective properties.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 28;12(9):e0184483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184483. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28957336 Free PMC article.
-
Methanol extract and fraction of Anchomanes difformis root tuber modulate liver mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore opening in rats.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2020 Mar-Apr;10(2):190-201. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2020. PMID: 32257891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim KW, Ha KT, Park CS, Jin UH, Chang HW, Lee IS, Kim CH. Polygonumcuspidatum, compared with baicalin and berberine, inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expressions in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Vascul Pharmacol. 2007;47:99–107. - PubMed
-
- Lamer-Zarawska E, Wiśniewska A, Błach-Olszewska Z. Anticancer properties of Scutellariabaicalensis root in aspect of innate immunity regulation. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2010;19:419–428.
-
- Li-Weber M. New therapeutic aspects of flavones: the anticancer properties of Scutellaria and its main active constituents wogonin, baicalein and baicalin. Cancer Treat Rev. 2008;35:57–68. - PubMed
-
- Ma Z, Otsuyama K, Liu S, Abroun S, Ishikawa H, Tsuyama N, Obata M, Li FJ, Zheng X, Maki Y, Miyamoto K, Kawano MM. Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria radix from Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang (HLJDT), leads to suppression of proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human myeloma cells. Blood. 2005;105:3312–8. - PubMed
-
- Malich G, Markovic B, Winder C. The sensitivity and specificity of the MTS tetrazolium assay for detecting the in vitro cytotoxicity of 20 chemicals using human cell lines. Toxicology. 1997;124:179–192. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
