Neonatal Hearing Screening Programme (NHSP): At A Rural Based Tertiary Care Centre
- PMID: 26693457
- PMCID: PMC4678260
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-015-0882-z
Neonatal Hearing Screening Programme (NHSP): At A Rural Based Tertiary Care Centre
Abstract
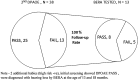
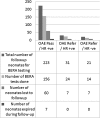
Deafness is the most common curable childhood handicap. It is a well recognised fact that unidentified hearing impairment can adversely affect optimal speech and language development and therefore academic, social and emotional development. Universal neonatal hearing screening programmes are implemented in many developed countries. However it is still in its early stage in India. The incidence of hearing impairment in India is 1-6 per thousand newborns screened (Paediatrics 19:155-165, 1998; Indian J Paediatr 74(6):545-549, 2007; Status of Disability in India, pp 172-185 2000). To determine the incidence of permanent hearing loss of moderate to evere variety in neonates taking care in a tertiary care rural based hospital in Gujarat. It was a non randomised observational study done for duration of 3 years. All neonates born in Shri Krishna Hospital underwent screening using two stage protocols with DPOAE test and final confirmation done with BERA. Total 2534 neonates were screened out of them 52 failed and 2482 (97.94 %) neonates passed in the 1st DPOAE test with 2.05 % refer rate. Total 7 (2 per 1000) neonates were detected with hearing impairment. 10 % neonates had one or other high risk factor. Out of high risk neonates, 1.8 % were diagnosed with hearing impairment in high risk group. Overall the follow-up rate was 72.7 %. Hospital based universal hearing screening of new born before discharge is feasible at a rural based tertiary care centre. Non specialist staff is invaluable in achieving a satisfactory referral rate with two stage hearing screening protocol. However, more efficacious tracking and follow up system is needed to improve the follow up rate for diagnosis.
Keywords: Congenital deafness; Impaired hearing; OAE-BERA; Universal neonatal hearing screening.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcome of Universal Neonatal Hearing Screening Programme at a Tertiary Care Centre: A Prospective Study.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Dec;74(Suppl 3):3813-3818. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02628-3. Epub 2021 May 17. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36742795 Free PMC article.
-
UNHS: A Decade Long Feasibility and Sustenance Study from a Tertiary Care Hospital in India.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Aug;74(Suppl 1):624-630. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02435-w. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36032914 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of Newborn Hearing at a Tertiary Care Hospital in South India.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019 Nov;71(Suppl 2):1383-1390. doi: 10.1007/s12070-018-1454-9. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019. PMID: 31750182 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal hearing screening.Eur J Pediatr. 1996 Jun;155(6):429-35. doi: 10.1007/BF01955176. Eur J Pediatr. 1996. PMID: 8789756 Review.
-
The need for universal neonatal hearing screening--some aspects of epidemiology and identification.Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999 Dec;88(432):69-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1999.tb01163.x. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10626584 Review.
Cited by
-
Cochlear dysfunction as an early biomarker of cognitive decline in normal hearing and mild hearing loss.Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2024 Feb 1;16(1):e12467. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12467. eCollection 2024 Jan-Mar. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38312514 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of Universal Neonatal Hearing Screening Programme at a Tertiary Care Centre: A Prospective Study.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Dec;74(Suppl 3):3813-3818. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02628-3. Epub 2021 May 17. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36742795 Free PMC article.
-
Experience, Challenges and Outcome of Implementing Universal New Born Hearing Screening in a Medical College Hospital Set Up.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Dec;74(Suppl 3):3841-3846. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-02633-6. Epub 2021 May 28. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36742634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachhman KR, Arvedson JV. Early identification and intervention for children who are hearing impaired. Paediatrics. 1998;19:155–165. - PubMed
-
- Rehabiltation Council of India; Status of Disability in India, 2000, New Delhi, 172–185
-
- Jewel J. Newborn hearing screening—experience at a tertiary hospital in northwest India. Int J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;2:211–214. doi: 10.4236/ijohns.2013.25044. - DOI
-
- WHO 2015 Media Centre; Deafness and Hearing Loss; Last updated February 2014. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs300/en/. Accessed 23 Feb 2015
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous