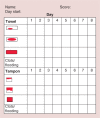
Outcome measures for heavy menstrual bleeding
- PMID: 26693585
- PMCID: PMC5779559
- DOI: 10.2217/whe.15.85
Outcome measures for heavy menstrual bleeding
Abstract
Heavy menstrual bleeding is one of the most commonly encountered gynecological problems. While accurate objective quantification of menstrual blood loss is of value in the research setting, it is the subjective assessment of blood loss that is of greater importance when assessing the severity of heavy menstrual bleeding and any subsequent response to treatment. In this review the various approaches to objective, subjective and semi-subjective assessment of menstrual blood loss will be discussed.
Keywords: abnormal uterine bleeding; heavy menstrual bleeding; menorrhagia; menstrual blood loss.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathophysiology of heavy menstrual bleeding.Womens Health (Lond). 2016 Jan;12(1):3-13. doi: 10.2217/whe.15.81. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Womens Health (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26695831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimation of menstrual blood loss volume based on menstrual diary and laboratory data.BMC Womens Health. 2012 Aug 20;12:24. doi: 10.1186/1472-6874-12-24. BMC Womens Health. 2012. PMID: 22906181 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy menstrual bleeding.Womens Health (Lond). 2016 Jan;12(1):1. doi: 10.2217/whe.15.71. Womens Health (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26767314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Daily menstrual blood loss and quality of life in women with heavy menstrual bleeding.Womens Health (Lond). 2012 Sep;8(5):503-11. doi: 10.2217/whe.12.36. Womens Health (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22934724
-
Menstrual Health as a Part of Preventive Health Care.Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2019 Sep;46(3):441-453. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2019.04.004. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 31378287 Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of methods to measure menstrual blood loss.BMC Womens Health. 2018 Aug 22;18(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12905-018-0627-8. BMC Womens Health. 2018. PMID: 30134884 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of recombinant bovine basic fibroblast growth factor to reduce hemorrhage after cervical loop electrosurgical excision procedure.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Jul 21;23(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02474-1. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37479994 Free PMC article.
-
Menstrual problems in chronic immune thrombocytopenia: A monthly challenge - a cohort study and review.Br J Haematol. 2022 Aug;198(4):753-764. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18291. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Br J Haematol. 2022. PMID: 35662003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron deficiency anemia in patients with heavy menstrual bleeding: The patients' perspective from diagnosis to treatment.Womens Health (Lond). 2025 Jan-Dec;21:17455057251321221. doi: 10.1177/17455057251321221. Womens Health (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40014696 Free PMC article.
-
Menstrual blood loss is an independent determinant of hemoglobin and ferritin levels in premenopausal blood donors.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2024 Aug;103(8):1645-1656. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14890. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2024. PMID: 38856303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hallberg L, Högdahl AM, Nilsson L, Rybo G. Menstrual blood loss – a population study. Variation at different ages and attempts to define normality. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 45(3), 320–351 (1966). - PubMed
-
- Janssen CA, Scholten PC, Heintz AP. A simple visual assessment technique to discriminate between menorrhagia and normal menstrual blood loss. Obstet. Gynecol. 85(6), 977–982 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Munro MG, Critchley HO, Fraser IS. The flexible FIGO classification concept for underlying causes of abnormal uterine bleeding. Semin. Reprod. Med. 29(5), 391–399 (2011). - PubMed
-
- NICE. Heavy Menstrual bleeding (2007). www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg44
-
- Chimbira TH, Anderson AB, Turnbull A. Relation between measured menstrual blood loss and patient's subjective assessment of loss, duration of bleeding, number of sanitary towels used, uterine weight and endometrial surface area. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 87(7), 603–609 (1980). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical