Butein inhibits metastatic behavior in mouse melanoma cells through VEGF expression and translation-dependent signaling pathway regulation
- PMID: 26694191
- PMCID: PMC4687249
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-015-0970-3
Butein inhibits metastatic behavior in mouse melanoma cells through VEGF expression and translation-dependent signaling pathway regulation
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Butein inhibits metastatic behavior in mouse melanoma cells through VEGF expression and translation-dependent signaling pathway regulation.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 May 29;23(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04010-y. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37248501 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Melanoma is an aggressive skin cancer and a predominant cause of skin cancer-related deaths. A previous study has demonstrated the ability of butein to inhibit tumor proliferation and invasion. However, the anti-metastatic mechanisms and in vivo effects of butein have not been fully elucidated.
Methods: MTT cell viability assays were used to evaluate the antitumor effects of butein in vitro. Cytotoxic effects of butein were measured by lactate dehydrogenase assay. Anti-migratory effects of butein were evaluated by two-dimensional scratch and transwell migration assays. Signaling transduction and VEGF-releasing assays were measured by Western blotting and ELISA. We also conducted an experimental analysis of the metastatic potential of tumor cells injected into the tail vein of C57BL/6 mice.
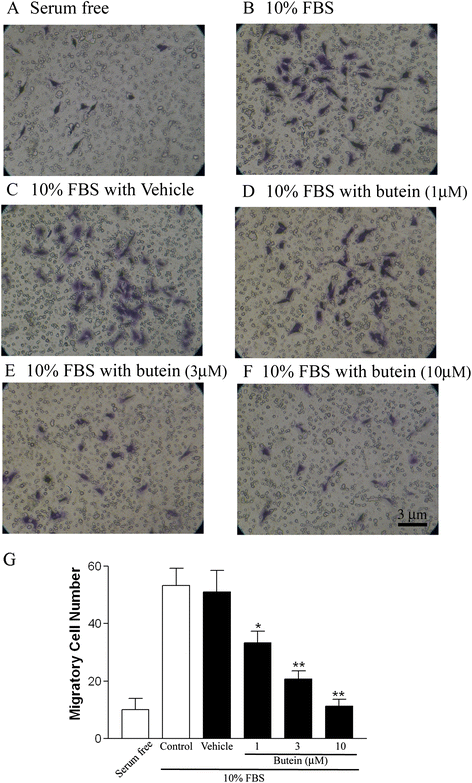
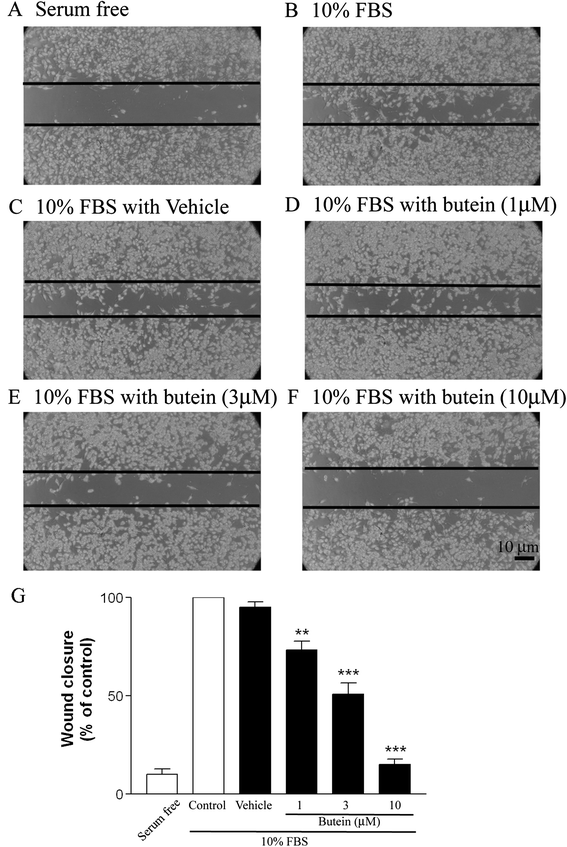
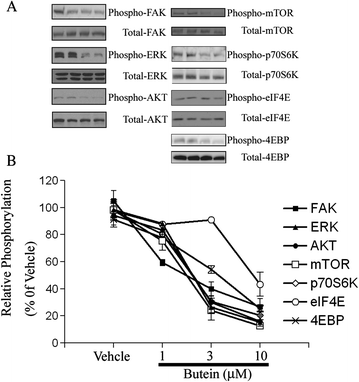
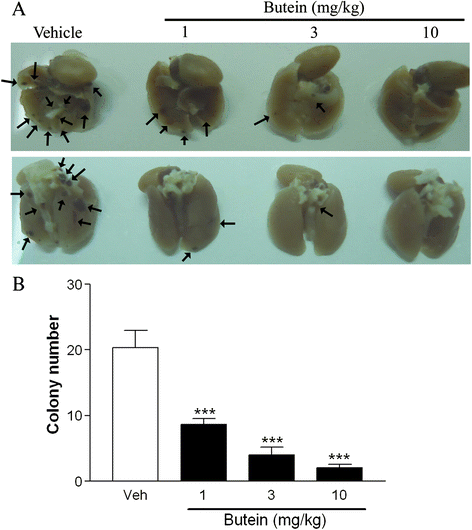
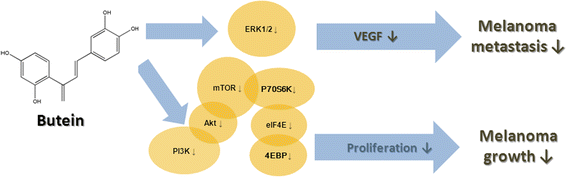
Results: We first demonstrated the effect of butein on cell viability at non-cytotoxic concentrations (1, 3, and 10 μM). In vitro, butein was found to inhibit the migration of B16F10 cells in a concentration-dependent manner using transwell and scratch assays. Butein had a dose-dependent effect on focal adhesion kinase, Akt, and ERK phosphorylation in B16F10 cells. Butein efficiently inhibited the mTOR/p70S6K translational inhibition machinery and decreased the production of VEGF in B16F10 cells. Furthermore, the in vivo antitumor effects of butein were demonstrated using a pulmonary metastasis model.
Conclusion: The results of the present study indicate the potential utility of butein in the treatment of melanoma.
Figures


References
-
- Mayer JE, Swetter SM, Fu T, Geller AC. Screening, early detection, education, and trends for melanoma: current status (2007-2013) and future directions: Part I. Epidemiology, high-risk groups, clinical strategies, and diagnostic technology. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71(4):599. - PubMed
-
- Chang JW. Cutaneous melanoma: Taiwan experience and literature review. Chang Gung Med J. 2010;33(6):602–612. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

