Does Reduction of Number of Intradetrusor Injection Sites of aboBoNTA (Dysport®) Impact Efficacy and Safety in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity?
- PMID: 26694464
- PMCID: PMC4690145
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins7124896
Does Reduction of Number of Intradetrusor Injection Sites of aboBoNTA (Dysport®) Impact Efficacy and Safety in a Rat Model of Neurogenic Detrusor Overactivity?
Abstract
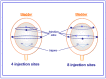
Intradetrusor injections of Botulinum toxin A-currently onabotulinumtoxinA-is registered as a second-line treatment to treat neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO). The common clinical practice is 30 × 1 mL injections in the detrusor; however, protocols remain variable and standardization is warranted. The effect of reducing the number of injection sites of Dysport(®) abobotulinumtoxinA (aboBoNTA) was assessed in the spinal cord-injured rat (SCI). Nineteen days post-spinalization, female rats received intradetrusor injections of saline or aboBoNTA 22.5 U distributed among four or eight sites. Two days after injection, continuous cystometry was performed in conscious rats. Efficacy of aboBoNTA 22.5 U was assessed versus aggregated saline groups on clinically-relevant parameters: maximal pressure, bladder capacity, compliance, voiding efficiency, as well as amplitude, frequency, and volume threshold for nonvoiding contractions (NVC). AboBoNTA 22.5 U significantly decreased maximal pressure, without affecting voiding efficiency. Injected in four sites, aboBoNTA significantly increased bladder capacity and compliance while only the latter when in eight sites. AboBoNTA significantly reduced NVC frequency and amplitude. This preclinical investigation showed similar inhibiting effects of aboBoNTA despite the number of sites reduction. Further studies are warranted to optimize dosing schemes to improve the risk-benefit ratio of BoNTA-based treatment modalities for NDO and further idiopathic overactive bladder.
Keywords: abobotulinumtoxinA; injection procedure; injection site number; neurogenic detrusor overactivity; spinal-cord injury.
Figures

References
-
- Schurch B., Stohrer M., Kramer G., Schmid D.M., Gaul G., Hauri D. Botulinum-A toxin for treating detrusor hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured patients: A new alternative to anticholinergic drugs? Preliminary results. J. Urol. 2000;164:692–697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

