Anti-aggressive effects of the selective high-efficacy 'biased' 5-HT₁A receptor agonists F15599 and F13714 in male WTG rats
- PMID: 26694810
- PMCID: PMC4759229
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-015-4173-x
Anti-aggressive effects of the selective high-efficacy 'biased' 5-HT₁A receptor agonists F15599 and F13714 in male WTG rats
Abstract
Background: The serotonin (5-HT) deficiency hypothesis of aggression is being seriously challenged by pharmacological data showing robust anti-aggressive effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonists in dose ranges that concomitantly inhibit 5-HT neurotransmission. Hence, an adequate interpretation of the role of 5-HT activity in regulating aggression depends on elucidating the predominant site of action, i.e., raphe presynaptic autoreceptors versus forebrain postsynaptic heteroreceptors, of these 5-HT1A receptor agonists.
Objectives: The present experiments investigated the anti-aggressive properties of the selective 5-HT1A receptor agonists F15599 that preferentially target postsynaptic 5-HT1A heteroreceptors in the frontal cortex and F13714 that more preferentially activates raphe somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors.
Methods: Both 'biased' agonists were acutely administered intraperitoneally in aggressive resident male WTG rats confronting an intruder.
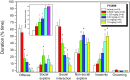
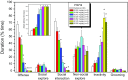
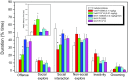
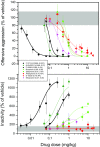
Results: Systemic administration of F15599 and F13714 exerted very potent (ID50 = 0.095 and 0.0059 mg/kg, respectively) anti-aggressive effects. At 4.5-fold higher dose ranges, the anti-aggressive effects were accompanied by concomitant motor inactivity and/or reduction of social engagement. Pretreatment with WAY-100635 counteracted the behavioural effects of both agonists.
Conclusions: Overall, the qualitatively similar but quantitatively different anti-aggressive profiles of F15599 and F13714 largely correspond to their distinct 5-HT1A receptor binding/activation potencies. Moreover, the marked anti-aggressive potency of F13714 adds additional support for a critical role of raphe somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors, and hence phasic 5-HT neuron activity, in the initiation/execution of aggressive actions.
Keywords: 5-HT1A; Aggressive behaviour; Autoreceptors; Dorsal Raphe; F13714; F15599; Heteroreceptors; Serotonin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Divergent effects of the 'biased' 5-HT1 A receptor agonists F15599 and F13714 in a novel object pattern separation task.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 May;172(10):2532-43. doi: 10.1111/bph.13071. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25572672 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptor Biased Agonists, F13714 and F15599, on Striatal Neurotransmitter Levels Following L-DOPA Administration in Hemi-Parkinsonian Rats.Neurochem Res. 2018 May;43(5):1035-1046. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-2514-y. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 29572645
-
Discriminative stimulus properties of the 5-HT1A receptor biased agonists NLX-101 and F13714, in rats trained to discriminate 8-OH-DPAT from saline.Behav Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 1;32(8):652-659. doi: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000659. Behav Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34751175 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptor agonists and aggression: a pharmacological challenge of the serotonin deficiency hypothesis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Dec 5;526(1-3):125-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.09.065. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16310183 Review.
-
Translating biased agonists from molecules to medications: Serotonin 5-HT1A receptor functional selectivity for CNS disorders.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jan;229:107937. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107937. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34174274 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of somatodendritic 5-HT1A autoreceptors reduces the acquisition and expression of cued fear in the rat fear-potentiated startle test.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Apr;236(4):1171-1185. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5124-0. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30539269 Free PMC article.
-
Linking organismal growth, coping styles, stress reactivity, and metabolism via responses against a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in an insect.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 5;8(1):8599. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26722-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29872133 Free PMC article.
-
Marmoset Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptor Mapping with a Biased Agonist PET Probe 18F-F13714: Comparison with an Antagonist Tracer 18F-MPPF in Awake and Anesthetized States.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Dec 30;19(12):pyw079. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw079. Print 2016 Dec. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27608810 Free PMC article.
-
Tryptophan hydroxylase 2 deficiency alters autism-related behavioural phenotypes in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20522. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05684-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594285 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Studies on the Role of 5-HT1 A Receptors in Male Sexual Behavior of Wildtype and Serotonin Transporter Knockout Rats.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Mar 31;14:40. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00040. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32296313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assié MB, Lomenech H, Ravailhe V, Faucillon V, Newman-Tancredi A. Rapid desensitization of somatodendritic 5-HT1A receptors by chronic administration of the high-efficacy 5-HT1A agonist, F13714: a microdialysis study in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;149:170–178. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706859. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Assié MB, Bardin L, Auclair AL, Carilla-Durand E, Depoortère R, Koek W, Kleven MS, Colpaert F, Vacher B, Newman-Tancredi A. F15599, a highly selective post-synaptic 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist: in-vivo profile in behavioural models of antidepressant and serotonergic activity. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13(10):1285–1298. doi: 10.1017/S1461145709991222. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

