In vivo single-particle imaging of nuclear mRNA export in budding yeast demonstrates an essential role for Mex67p
- PMID: 26694837
- PMCID: PMC4687877
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201503135
In vivo single-particle imaging of nuclear mRNA export in budding yeast demonstrates an essential role for Mex67p
Abstract
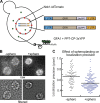
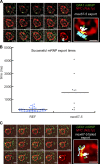
Many messenger RNA export proteins have been identified; yet the spatial and temporal activities of these proteins and how they determine directionality of messenger ribonucleoprotein (mRNP) complex export from the nucleus remain largely undefined. Here, the bacteriophage PP7 RNA-labeling system was used in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to follow single-particle mRNP export events with high spatial precision and temporal resolution. These data reveal that mRNP export, consisting of nuclear docking, transport, and cytoplasmic release from a nuclear pore complex (NPC), is fast (∼ 200 ms) and that upon arrival in the cytoplasm, mRNPs are frequently confined near the nuclear envelope. Mex67p functions as the principal mRNP export receptor in budding yeast. In a mex67-5 mutant, delayed cytoplasmic release from NPCs and retrograde transport of mRNPs was observed. This proves an essential role for Mex67p in cytoplasmic mRNP release and directionality of transport.
© 2015 Smith et al.
Figures


References
-
- Bachi A., Braun I.C., Rodrigues J.P., Panté N., Ribbeck K., von Kobbe C., Kutay U., Wilm M., Görlich D., Carmo-Fonseca M., and Izaurralde E.. 2000. The C-terminal domain of TAP interacts with the nuclear pore complex and promotes export of specific CTE-bearing RNA substrates. RNA. 6:136–158. 10.1017/S1355838200991994 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

