Epidemiology of Haemophilus ducreyi Infections
- PMID: 26694983
- PMCID: PMC4696685
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2201.150425
Epidemiology of Haemophilus ducreyi Infections
Erratum in
- Emerg Infect Dis. 2016 Feb;22(2):356
-
Correction: Vol. 22, No. 1.Emerg Infect Dis. 2016 Feb;22(2):356. doi: 10.3201/eid2202.C12202. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 31265533 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The global epidemiology of Haemophilus ducreyi infections is poorly documented because of difficulties in confirming microbiological diagnoses. We evaluated published data on the proportion of genital and nongenital skin ulcers caused by H. ducreyi before and after introduction of syndromic management for genital ulcer disease (GUD). Before 2000, the proportion of GUD caused by H. ducreyi ranged from 0.0% to 69.0% (35 studies in 25 countries). After 2000, the proportion ranged from 0.0% to 15.0% (14 studies in 13 countries). In contrast, H. ducreyi has been recently identified as a causative agent of skin ulcers in children in the tropical regions; proportions ranged from 9.0% to 60.0% (6 studies in 4 countries). We conclude that, although there has been a sustained reduction in the proportion of GUD caused by H. ducreyi, this bacterium is increasingly recognized as a major cause of nongenital cutaneous ulcers.
Keywords: Haemophilus ducreyi; bacteria; chancroid; epidemiology; genital ulcer disease; genital ulcers; nongenital cutaneous infections; sexually transmitted infections; skin ulcers.
Figures
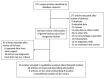
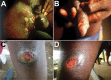
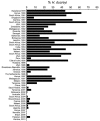
References
-
- Schmid G, Steen R, N’Dowa F. Control of bacterial sexually transmitted diseases in the developing world is possible. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:1313–5 and. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

