A "Double-Edged" Scaffold: Antitumor Power within the Antibacterial Quinolone
- PMID: 26695512
- PMCID: PMC4997924
- DOI: 10.2174/0929867323666151223095839
A "Double-Edged" Scaffold: Antitumor Power within the Antibacterial Quinolone
Abstract
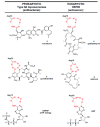
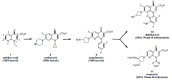
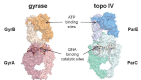
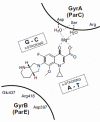
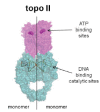
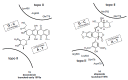
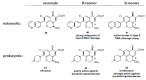
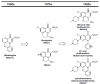
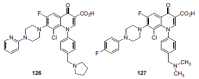
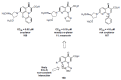
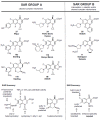
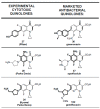
In the late 1980s, reports emerged describing experimental antibacterial quinolones having significant potency against eukaryotic Type II topoisomerases (topo II) and showing cytotoxic activity against tumor cell lines. As a result, several pharmaceutical companies initiated quinolone anticancer programs to explore the potential of this class in comparison to conventional human topo II inhibiting antitumor drugs such as doxorubicin and etoposide. In this review, we present a modern re-evaluation of the anticancer potential of the quinolone class in the context of today's predominantly pathway-based (rather than cytotoxicity-based) oncology drug R&D environment. The quinolone eukaryotic SAR is comprehensively discussed, contrasted with the corresponding prokaryotic data, and merged with recent structural biology information which is now beginning to help explain the basis for that SAR. Quinolone topo II inhibitors appear to be much less susceptible to efflux-mediated resistance, a current limitation of therapy with conventional agents. Recent advances in the biological understanding of human topo II isoforms suggest that significant progress might now be made in overcoming two other treatment-limiting disadvantages of conventional topo II inhibitors, namely cardiotoxicity and drug-induced secondary leukemias. We propose that quinolone class topo II inhibitors could have a useful future therapeutic role due to the continued need for effective topo II drugs in many cancer treatment settings, and due to the recent biological and structural advances which can now provide, for the first time, specific guidance for the design of a new class of inhibitors potentially superior to existing agents.
Figures
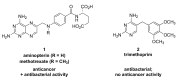
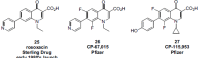
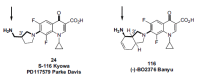
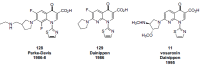

Similar articles
-
Recent advancements in the medicinal chemistry of bacterial type II topoisomerase inhibitors.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104266. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104266. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33142421 Review.
-
Novel ciprofloxacin hybrids using biology oriented drug synthesis (BIODS) approach: Anticancer activity, effects on cell cycle profile, caspase-3 mediated apoptosis, topoisomerase II inhibition, and antibacterial activity.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Apr 25;150:403-418. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.026. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29547830
-
The quinolone family: from antibacterial to anticancer agents.Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003 Nov;3(6):439-50. doi: 10.2174/1568011033482279. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents. 2003. PMID: 14529452 Review.
-
The Current Case of Quinolones: Synthetic Approaches and Antibacterial Activity.Molecules. 2016 Mar 28;21(4):268. doi: 10.3390/molecules21040268. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27043501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the development of dual topoisomerase I and II inhibitors as anticancer drugs.Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(35):4270-90. doi: 10.2174/092986710793361252. Curr Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20939813 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Ciprofloxacin on Susceptibility to Aortic Dissection and Rupture in Mice.JAMA Surg. 2018 Sep 1;153(9):e181804. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.1804. Epub 2018 Sep 19. JAMA Surg. 2018. PMID: 30046809 Free PMC article.
-
Newly Substituted Anilino-Fluoroquinolones with Proliferation Inhibition Potential against a Panel of Cancer Cell Lines.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Jul 1;23(7):2507-2521. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.7.2507. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 35901360 Free PMC article.
-
Kynurenine-3-monooxygenase (KMO) broadly inhibits viral infections via triggering NMDAR/Ca2+ influx and CaMKII/ IRF3-mediated IFN-β production.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Mar 2;18(3):e1010366. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010366. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35235615 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Class of Functionalized Synthetic Fluoroquinolones with Dual Antiproliferative - Antimicrobial Capacities.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021 Apr 1;22(4):1075-1086. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2021.22.4.1075. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2021. PMID: 33906299 Free PMC article.
-
Quinolin-4-ones: Methods of Synthesis and Application in Medicine.Molecules. 2025 Jan 3;30(1):163. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010163. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39795219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ehrlich P. Address Delivered at the Dedication of the Georg-Speyer-Haus. In: Himmelweit F., editor. The Collected Papers of Paul Ehrlich. Vol. III. UK: Pergamon Press, Ltd.; 1960. pp. 53–63.
-
- Drews J. Paul Ehrlich: magister mundi. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3:797–801. - PubMed
-
- Weber C.M. Der Freischütz.
-
- Grundmann K. Emil von Behring: the founder of serum therapy.
-
- Strohl W.R. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Past, Present, and Future. In: Zhiqiang A., editor. Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2009. pp. 3–50.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

