Neuroimmune Function and the Consequences of Alcohol Exposure
- PMID: 26695754
- PMCID: PMC4590627
Neuroimmune Function and the Consequences of Alcohol Exposure
Abstract
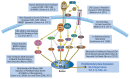
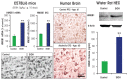
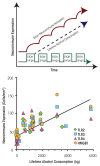
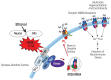
Induction of neuroimmune genes by binge drinking increases neuronal excitability and oxidative stress, contributing to the neurobiology of alcohol dependence and causing neurodegeneration. Ethanol exposure activates signaling pathways featuring high-mobility group box 1 and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), resulting in induction of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, which regulates expression of several cytokine genes involved in innate immunity, and its target genes. This leads to persistent neuroimmune responses to ethanol that stimulate TLRs and/or certain glutamate receptors (i.e., N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors). Alcohol also alters stress responses, causing elevation of peripheral cytokines, which further sensitize neuroimmune responses to ethanol. Neuroimmune signaling and glutamate excitotoxicity are linked to alcoholic neurodegeneration. Models of alcohol abuse have identified significant frontal cortical degeneration and loss of hippocampal neurogenesis, consistent with neuroimmune activation pathology contributing to these alcohol-induced, long-lasting changes in the brain. These alcohol-induced long-lasting increases in brain neuroimmune-gene expression also may contribute to the neurobiology of alcohol use disorder.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of neuroimmune gene induction in alcoholism.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 May;233(9):1543-57. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3906-1. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 25787746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol, HMGB1, and Innate Immune Signaling in the Brain.Alcohol Res. 2024 Aug 8;44(1):04. doi: 10.35946/arcr.v44.1.04. eCollection 2024. Alcohol Res. 2024. PMID: 39135668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroimmune basis of alcoholic brain damage.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;118:315-57. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-801284-0.00010-5. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25175868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of neuroimmune signaling in alcoholism.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Aug 1;122:56-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.031. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28159648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of the Innate Immune Response in the Actions of Ethanol on the Central Nervous System.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Nov;40(11):2260-2270. doi: 10.1111/acer.13208. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 27650785 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune activation and neuroinflammation in alcohol use and HIV infection: evidence for shared mechanisms.Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017 Jan;43(1):7-23. doi: 10.1080/00952990.2016.1211667. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2017. PMID: 27532935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PCSK9 and the Gut-Liver-Brain Axis: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Immune Regulation in Alcohol Use Disorder.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 18;10(8):1758. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081758. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33919550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Embryonic Heat Conditioning Induces TET-Dependent Cross-Tolerance to Hypothalamic Inflammation Later in Life.Front Genet. 2020 Aug 5;11:767. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00767. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32849788 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal and adolescent alcohol exposure programs immunity across the lifespan: CNS-mediated regulation.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 May;216:173390. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173390. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 35447157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased alcohol self-administration following repeated Toll-like receptor 3 agonist treatment in male and female rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 May;216:173379. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173379. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 35395252 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acheson SK, Stein RM, Swartzwelder HS. Impairment of semantic and figural memory by acute ethanol: Age-dependent effects. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 1998;22(7):1437–1442. - PubMed
-
- Carr LG, Spence JP, Peter Eriksson CJ, et al. AA and ANA rats exhibit the R100Q mutation in the GABAA receptor alpha 6 subunit. Alcohol. 2003;31(1–2):93–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

