Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations in Children Progressing to Autoimmunity and Clinical Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 26695863
- PMCID: PMC4880127
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2015-3504
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations in Children Progressing to Autoimmunity and Clinical Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Context: The role of vitamin D in the development of type 1 diabetes (T1D) remains controversial.
Objective: The objective of the investigation was to study whether there are detectable differences in serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) concentrations between children who later progressed to T1D (cases) and matched children who remained nondiabetic and negative for islet autoantibodies (controls) when followed up from birth until disease onset.
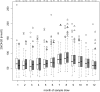
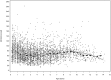
Design: A total of 3702 prospective serum samples from 252 children were measured for 25(OH)D from the age of 3 months onward using an enzyme immunoassay. Differences between the groups were compared by the mixed-model analysis of variance.
Setting: T1D prediction and prevention study clinics in Turku, Oulu, and Tampere University Hospitals, Finland, participated in the study.
Participants: By the end of 2012, all 126 case children were diagnosed with T1D. The control children (n = 126) were matched for age, sex, study site, and human leukocyte antigen-HLA-DQ-conferred risk for T1D.
Main outcome measure: Median circulating 25(OH)D concentration (nanomoles per liter) was measured.
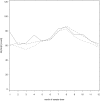
Results: The patterns of variation in circulating 25(OH)D concentrations were similar between cases and controls and did not correlate with the age at seroconversion to autoantibody positivity (P = .79) or disease onset (P = .13). The median concentration of all collected samples did not differ between case and control children (66.6 nmol/L [range 14.0-262.8] vs 67.4 nmol/L [range 19.9-213.0]) P = .56).
Conclusions: This study shows that serum 25(OH)D concentrations are not associated with the development of T1D in Finland.
Figures
References
-
- Littorin B, Blom P, Scholin A, et al. Lower levels of plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D among young adults at diagnosis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes compared with control subjects: results from the nationwide Diabetes Incidence Study in Sweden (DISS). Diabetologia. 2006;49(12):2847–2852. - PubMed
-
- Pozzilli P, Manfrini S, Crino A, et al. Low levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Horm Metab Res. 2005;37(11):680–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

