Evolving function and potential of pancreatic alpha cells
- PMID: 26696515
- PMCID: PMC4690008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.beem.2015.10.002
Evolving function and potential of pancreatic alpha cells
Abstract
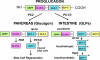
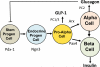
The alpha cells that co-occupy the islets in association with beta cells have been long recognized as the source of glucagon, a hyperglycemia-producing and diabetogenic hormone. Although the mechanisms that control the functions of alpha cells, glucagon secretion, and the role of glucagon in diabetes have remained somewhat enigmatic over the fifty years since their discovery, seminal findings during the past few years have moved alpha cells into the spotlight of scientific discovery. These findings obtained largely from studies in mice are: Alpha cells have the capacity to trans-differentiate into insulin-producing beta cells. Alpha cells contain a GLP-1 generating system that produces GLP-1 locally for paracrine actions within the islets that likely promotes beta cell growth and survival and maintains beta cell mass. Impairment of glucagon signaling both prevents the occurrence of diabetes in conditions of the near absence of insulin and expands alpha cell mass. Alpha cells appear to serve as helper cells or guardians of beta cells to ensure their health and well-being. Of potential relevance to the possibility of promoting the transformation of alpha to beta cells is the observation that impairment of glucagon signaling leads to a marked increase in alpha cell mass in the islets. Such alpha cell hyperplasia provides an increased supply of alpha cells for their transdifferentiation into new beta cells. In this review we discuss these recent discoveries from the perspective of their potential relevance to the treatment of diabetes.
Keywords: GLP-1; alpha cells; beta cells; diabetes; proglucagon; transdifferentiation.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Increases β-Cell Regeneration by Promoting α- to β-Cell Transdifferentiation.Diabetes. 2018 Dec;67(12):2601-2614. doi: 10.2337/db18-0155. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 30257975
-
Glucagon is essential for alpha cell transdifferentiation and beta cell neogenesis.Development. 2015 Apr 15;142(8):1407-17. doi: 10.1242/dev.117911. Development. 2015. PMID: 25852199 Free PMC article.
-
Increased alpha and beta cell mass during mouse pregnancy is not dependent on transdifferentiation.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Mar;246(5):617-628. doi: 10.1177/1535370220972686. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33231513 Free PMC article.
-
α-cell role in β-cell generation and regeneration.Islets. 2012 May-Jun;4(3):188-98. doi: 10.4161/isl.20500. Islets. 2012. PMID: 22847495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of transcription factors in the transdifferentiation of pancreatic islet cells.J Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Apr;54(2):R103-17. doi: 10.1530/JME-14-0290. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25791577 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in pancreatic α-cell transdifferentiation for diabetes therapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 22;16:1551372. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1551372. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39911402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental Programming of Obesity and Diabetes in Mouse, Monkey, and Man in 2018: Where Are We Headed?Diabetes. 2018 Nov;67(11):2137-2151. doi: 10.2337/dbi17-0011. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 30348820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Lactobacillus paraplantarum BGCG11 on Pancreatic and Duodenum Function in Diabetic Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 13;25(14):7697. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147697. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062940 Free PMC article.
-
EpiCRISPR targeted methylation of Arx gene initiates transient switch of mouse pancreatic alpha to insulin-producing cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 16;14:1134478. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1134478. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37008919 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of long-acting GIP, xenin and oxyntomodulin peptide analogues on alpha-cell transdifferentiation in insulin-deficient diabetic GluCreERT2;ROSA26-eYFP mice.Peptides. 2020 Mar;125:170205. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2019.170205. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Peptides. 2020. PMID: 31738969 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

