Slow Physical Growth, Delayed Reflex Ontogeny, and Permanent Behavioral as Well as Cognitive Impairments in Rats Following Intra-generational Protein Malnutrition
- PMID: 26696810
- PMCID: PMC4672086
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00446
Slow Physical Growth, Delayed Reflex Ontogeny, and Permanent Behavioral as Well as Cognitive Impairments in Rats Following Intra-generational Protein Malnutrition
Abstract
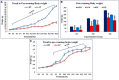
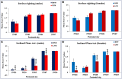
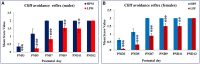
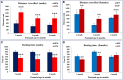
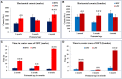
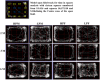
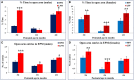
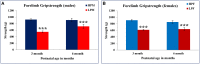
Environmental stressors including protein malnutrition (PMN) during pre-, neo- and post-natal age have been documented to affect cognitive development and cause increased susceptibility to neuropsychiatric disorders. Most studies have addressed either of the three windows and that does not emulate the clinical conditions of intra-uterine growth restriction (IUGR). Such data fail to provide a complete picture of the behavioral alterations in the F1 generation. The present study thus addresses the larger window from gestation to F1 generation, a new model of intra-generational PMN. Naive Sprague Dawley (SD) dams pre-gestationally switched to LP (8% protein) or HP (20% protein) diets for 45 days were bred and maintained throughout gestation on same diets. Pups born (HP/LP dams) were maintained on the respective diets post-weaningly. The present study aimed to show the sex specific differences in the neurobehavioral evolution and behavioral phenotype of the HP/LP F1 generation pups. A battery of neurodevelopmental reflex tests, behavioral (Open field and forelimb gripstrength test), and cognitive [Elevated plus maze (EPM) and Morris water maze (MWM)] assays were performed. A decelerated growth curve with significantly restricted body and brain weight, delays in apparition of neuro-reflexes and poor performance in the LP group rats was recorded. Intra-generational PMN induced poor habituation-with-time in novel environment exploration, low anxiety and hyperactive like profile in open field test in young and adult rats. The study revealed poor forelimb neuromuscular strength in LP F1 pups till adulthood. Group occupancy plots in MWM test revealed hyperactivity with poor learning, impaired memory retention and integration, thus modeling the signs of early onset Alzehemier phenotype. In addition, a gender specific effect of LP diet with severity in males and favoring female sex was also noticed.
Keywords: Morris water maze; anxiety; cliff avoidance; elevated plus maze; intra-generational protein malnutrition; open field test.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Developmental Changes in Oligodendrocyte Genesis, Myelination, and Associated Behavioral Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Intra-generational Protein Malnutrition.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jan;56(1):595-610. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1065-1. Epub 2018 May 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29752656
-
Multiple Early Life Stressors as Risk Factors for Neurodevelopmental Abnormalities in the F1 Wistar Rats.Brain Sci. 2023 Sep 22;13(10):1360. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13101360. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37891729 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of neurobehavioral and cognitive abilities of F1 progeny following dietary supplementation with Spirulina to protein malnourished mothers.Brain Behav Immun. 2020 Mar;85:69-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.08.181. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Brain Behav Immun. 2020. PMID: 31425827
-
Maternal voluntary physical activity attenuates delayed neurodevelopment in malnourished rats.Exp Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;102(11):1486-1499. doi: 10.1113/EP086400. Epub 2017 Sep 24. Exp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28833822
-
Severe Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury Induces Long-Term Sensorimotor Deficits, Anxiety-Like Behaviors and Cognitive Impairment in a Sex-, Age- and Task-Selective Manner in C57BL/6 Mice but Can Be Modulated by Neonatal Handling.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Feb 13;13:7. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00007. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30814939 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Neuronal changes and cognitive deficits in a multi-hit rat model following cumulative impact of early life stressors.Biol Open. 2020 Sep 24;9(9):bio054130. doi: 10.1242/bio.054130. Biol Open. 2020. PMID: 32878878 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal exposure to synergistic multiple stressors leads to cellular and behavioral deficits mimicking Schizophrenia-like pathology.Biol Open. 2022 Mar 15;11(3):bio058870. doi: 10.1242/bio.058870. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Biol Open. 2022. PMID: 35107124 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal diet and offspring anxiety: A scoping review.Transl Neurosci. 2022 Sep 6;13(1):275-290. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0242. eCollection 2022 Jan 1. Transl Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36128579 Free PMC article.
-
Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract Improves Cognitive Function in Rat Offspring Born to Protein-Deficient Mothers.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 3;13(2):346. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020346. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002759 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of socioeconomic and stimulus inequality on human brain physiology.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 2;11(1):7439. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85236-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33811239 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

