Calretinin as a Marker for Premotor Neurons Involved in Upgaze in Human Brainstem
- PMID: 26696837
- PMCID: PMC4677283
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2015.00153
Calretinin as a Marker for Premotor Neurons Involved in Upgaze in Human Brainstem
Abstract
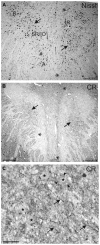
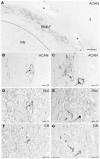
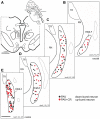
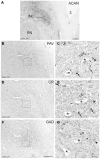
Eye movements are generated by different premotor pathways. Damage to them can cause specific deficits of eye movements, such as saccades. For correlative clinico-anatomical post-mortem studies of cases with eye movement disorders it is essential to identify the functional cell groups of the oculomotor system in the human brain by marker proteins. Based on monkey studies, the premotor neurons of the saccadic system can be identified by the histochemical markers parvalbumin (PAV) and perineuronal nets in humans. These areas involve the interstitial nucleus of Cajal (INC) and the rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle (RIMLF), which both contain premotor neurons for upgaze and downgaze. Recent monkey and human studies revealed a selective excitatory calretinin (CR)-positive input to the motoneurons mediating upgaze, but not to those for downgaze. Three premotor regions were identified as sources of CR input in monkey: y-group, INC and RIMLF. These findings suggest that the expression pattern of parvalbumin and CR may help to identify premotor neurons involved in up- or downgaze. In a post-mortem study of five human cases without neurological diseases we investigated the y-group, INC and RIMLF for the presence of parvalbumin and CR positive neurons including their co-expression. Adjacent thin paraffin sections were stained for the aggrecan (ACAN) component of perineuronal nets, parvalbumin or CR and glutamate decarboxylase. The comparative analysis of scanned thin sections of INC and RIMLF revealed medium-sized parvalbumin positive neurons with and without CR coexpression, which were intermingled. The parvalbumin/CR positive neurons in both nuclei are considered as excitatory premotor upgaze neurons. Accordingly, the parvalbumin-positive neurons lacking CR are considered as premotor downgaze neurons in RIMLF, but may in addition include inhibitory premotor upgaze neurons in the INC as indicated by co-expression of glutamate decarboxylase in a subpopulation. CR-positive neurons ensheathed by perineuronal nets in the human y-group are considered as the homolog premotor neurons described in monkey, projecting to superior rectus (SR) and inferior oblique (IO) motoneurons. In conclusion, combined immunostaining for parvalbumin, perineuronal nets and CR may well be suited for the specific identification and subsequent analysis of premotor upgaze pathways in clinical cases of isolated up- or downgaze deficits.
Keywords: interstitial nucleus of Cajal; oculomotor nucleus; rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle; saccadic burst neurons; y-group.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Premotor neurons for vertical eye movements in the rostral mesencephalon of monkey and human: histologic identification by parvalbumin immunostaining.J Comp Neurol. 1998 Mar 23;392(4):413-27. J Comp Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9514507
-
Sources of calretinin inputs to motoneurons of extraocular muscles involved in upgaze.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011 Sep;1233:91-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.06168.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011. PMID: 21950981 Free PMC article.
-
Calretinin inputs are confined to motoneurons for upward eye movements in monkey.J Comp Neurol. 2013 Oct 1;521(14):3154-66. doi: 10.1002/cne.23337. J Comp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23696443
-
[Central oculomotor circuits].Rev Neurol (Paris). 1985;141(5):349-70. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1985. PMID: 3901182 Review. French.
-
Nuclear, internuclear, and supranuclear ocular motor disorders.Handb Clin Neurol. 2011;102:319-31. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-52903-9.00018-2. Handb Clin Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21601072 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebellar projections to the macaque midbrain tegmentum: Possible near response connections.Vis Neurosci. 2021 May 12;38:E007. doi: 10.1017/S0952523821000067. Vis Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33977889 Free PMC article.
-
Macaque monkey trigeminal blink reflex circuits targeting levator palpebrae superioris motoneurons.J Comp Neurol. 2021 Oct;529(14):3389-3409. doi: 10.1002/cne.25198. Epub 2021 Jun 11. J Comp Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34101199 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of secondary vestibulo-ocular neurons in human based on their histochemical characteristics found in monkey.J Neurol. 2017 Mar;264(3):583-585. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8397-z. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28116496 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Histochemical Characterization of the Vestibular Y-Group in Monkey.Cerebellum. 2021 Oct;20(5):701-716. doi: 10.1007/s12311-020-01200-z. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Cerebellum. 2021. PMID: 33083961 Free PMC article.
-
Oculomotor and Vestibular Findings in Gaucher Disease Type 3 and Their Correlation with Neurological Findings.Front Neurol. 2018 Jan 15;8:711. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00711. eCollection 2017. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29379464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blazquez P., Partsalis A., Gerrits N. M., Highstein S. M. (2000). Input of anterior and posterior semicircular canal interneurons encoding head-velocity to the dorsal Y group of the vestibular nuclei. J. Neurophysiol. 83, 2891–2904. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

