Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy in Non-insertional Achilles Tendinopathy: The Efficacy is Reduced in 60-years Old People Compared to Young and Middle-Age Individuals
- PMID: 26696880
- PMCID: PMC4674567
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00228
Platelet Rich Plasma Therapy in Non-insertional Achilles Tendinopathy: The Efficacy is Reduced in 60-years Old People Compared to Young and Middle-Age Individuals
Abstract
Background: Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) has shown positive and long-lasting effects in patients with tendinopathies. However, information about age-related differences in the clinical outcome is limited. Aim of this retrospective study was to compare the efficacy of PRP therapy in young and elderly subjects suffering for Achilles tendinopathy.
Materials and method: Patients with recalcitrant non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy were enrolled. Clinical (VISA-A) and instrumental (ultrasonography) data were collected at baseline and after 1, 3, 6, and 12 months. PRP injections (once a week for 3 weeks) were performed in sterile conditions and under ultrasound (US) control.
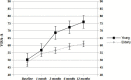
Results: Forty-four subjects (29 young: mean age 39.5 ± 6.9; 15 elderly: mean age 61.5 ± 5.3) were retrospectively evaluated. At baseline, no significant differences were observed in the clinical and US parameters. Throughout the whole length of the study, a significant increase of VISA-A score was seen in both groups (from 50.3 ± 8.8 to 76.1 ± 6.6 in the young group, and from 48.7 ± 7.6 to 61.1 ± 9.4 in the elderly group); however, the infra-groups comparison showed better results in young patients, compared to the aged counterpart.
Conclusion: Our results show that PRP is less effective in aged people. This finding can be ascribed to several biochemical and biomechanical differences documented in tendons of young and elderly subjects (reduced number and functionality of tenocytes and tenoblasts), which becomes more evident in the long-term tissue healing. However, prospective trials, using different PRP preparations and enrolling a larger number of subjects, are needed to draw more sound and definitive conclusions.
Keywords: Achilles tendinopathy; aging; platelet rich plasma; ultrasonography; young.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term beneficial effects of platelet-rich plasma for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy.Foot Ankle Surg. 2015 Sep;21(3):178-81. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2014.11.005. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Foot Ankle Surg. 2015. PMID: 26235856
-
Intratendinous adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction (SVF) injection provides a safe, efficacious treatment for Achilles tendinopathy: results of a randomized controlled clinical trial at a 6-month follow-up.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018 Jul;26(7):2000-2010. doi: 10.1007/s00167-017-4479-9. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018. PMID: 28251260 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of High-Volume Injection, Platelet-Rich Plasma, and Sham Treatment in Chronic Midportion Achilles Tendinopathy: A Randomized Double-Blinded Prospective Study.Am J Sports Med. 2017 Jul;45(9):2034-2043. doi: 10.1177/0363546517702862. Epub 2017 May 22. Am J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28530451 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma injections for treating Achilles tendonitis : Systematic review of high-quality randomized controlled trials.Orthopade. 2019 Sep;48(9):784-791. doi: 10.1007/s00132-019-03711-y. Orthopade. 2019. PMID: 30937491 English.
-
The use of PRP in treatment of Achilles Tendinopathy: A systematic review of literature. Study design: Systematic review of literature.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2020 Jun 1;55:320-326. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.04.042. eCollection 2020 Jul. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32566217 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Orthobiologics in Achilles Tendinopathy: A Review.Life (Basel). 2022 Mar 9;12(3):399. doi: 10.3390/life12030399. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35330150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-rich plasma: combinational treatment modalities for musculoskeletal conditions.Front Med. 2018 Apr;12(2):139-152. doi: 10.1007/s11684-017-0551-6. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Front Med. 2018. PMID: 29058255 Review.
-
Why PRP works only on certain patients with tennis elbow? Is PDGFB gene a key for PRP therapy effectiveness? A prospective cohort study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Aug 18;22(1):710. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04593-y. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021. PMID: 34407802 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet Concentrates in Musculoskeletal Medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 16;21(4):1328. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041328. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32079117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in Achilles tendon risk-analyzing rupture factors for enhanced injury prevention and clinical guidance: Current implications of regenerative medicine.J Orthop Translat. 2024 Nov 4;49:289-307. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.08.024. eCollection 2024 Nov. J Orthop Translat. 2024. PMID: 39559294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abate M., Di Gregorio P., Schiavone C., Salini V., Tosi U., Muttini A. (2012). Platelet rich plasma in tendinopathies: how to explain the failure. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 25 325–334. - PubMed
-
- Andia I., Abate M. (2012). Platelet-rich plasma injections for tendinopathy and osteoarthritis. Int. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 7 397–412. 10.2217/ijr.12.36 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous