Parenting Styles, Feeding Styles, Feeding Practices, and Weight Status in 4-12 Year-Old Children: A Systematic Review of the Literature
- PMID: 26696920
- PMCID: PMC4677105
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01849
Parenting Styles, Feeding Styles, Feeding Practices, and Weight Status in 4-12 Year-Old Children: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Abstract
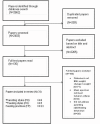
Childhood is a critical period in the development of obesity. Eating patterns established early in life track into later life. Therefore, parental approaches to feeding in their general parenting style, feeding styles, and specific feeding practices will have a profound impact on how children eat and grow. A systematic research review following PRISMA guidelines was conducted to identify, discuss and integrate recent research investigating the relationship between parenting styles, feeding styles, feeding practices, and body mass index (BMI) in children. Medline (Ovid), PsycINFO, Web of Science, and Food Science and Technology Abstracts were systematically searched using sensitive search strategies. Studies were limited to papers published in English between 2010 and February 2015 with participants aged 4-12 years old with outcomes including obesity, change in weight, or BMI. The search yielded 31 relevant quantitative peer-reviewed papers meeting all inclusion criteria: seven longitudinal, 23 cross-sectional, one randomized control trial. Associations between parenting style and child BMI were strongest and most consistent within the longitudinal studies. Uninvolved, indulgent or highly protective parenting was associated with higher child BMI, whereas authoritative parenting was associated with a healthy BMI. Similarly for feeding styles, indulgent feeding was consistently associated with risk of obesity within cross-sectional studies. Specific feeding practices such as restriction and pressure to eat were linked to BMI, especially within cross-sectional studies. Where child traits were measured, the feeding practice appeared to be responsive to the child, therefore restriction was applied to children with a high BMI and pressure to eat applied to children with a lower BMI. Behaviors and styles that are specific to the feeding context are consistently associated with child BMI. However, since obesity emerges over time, it is through longitudinal, carefully measured (through questionnaire and observation) studies which take account of child appetite and temperament that the association between parenting style, feeding style, specific feeding practices, and child obesity will be understood.
Keywords: children; feeding practices; feeding styles; obesity; parenting styles.
Figures

References
-
- Birch L. L., Fisher J. O. (1998). Development of eating behaviors among children and adolescents. Pediatrics 101(Suppl. 2), 539–549. - PubMed
-
- Birch L. L., Fisher J. O., Grimm-Thomas K., Markey C. N., Sawyer R., Johnson S. L. (2001). Confirmatory factor analysis of the Child Feeding Questionnaire: a measure of parental attitudes, beliefs and practices about child feeding and obesity proneness. Appetite 36, 201–210. 10.1006/appe.2001.0398 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

