Rice Sheath Rot: An Emerging Ubiquitous Destructive Disease Complex
- PMID: 26697031
- PMCID: PMC4675855
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01066
Rice Sheath Rot: An Emerging Ubiquitous Destructive Disease Complex
Abstract
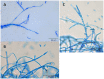
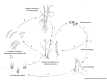
Around one century ago, a rice disease characterized mainly by rotting of sheaths was reported in Taiwan. The causal agent was identified as Acrocylindrium oryzae, later known as Sarocladium oryzae. Since then it has become clear that various other organisms can cause similar disease symptoms, including Fusarium sp. and fluorescent pseudomonads. These organisms have in common that they produce a range of phytotoxins that induce necrosis in plants. The same agents also cause grain discoloration, chaffiness, and sterility and are all seed-transmitted. Rice sheath rot disease symptoms are found in all rice-growing areas of the world. The disease is now getting momentum and is considered as an important emerging rice production threat. The disease can lead to variable yield losses, which can be as high as 85%. This review aims at improving our understanding of the disease etiology of rice sheath rot and mainly deals with the three most reported rice sheath rot pathogens: S. oryzae, the Fusarium fujikuroi complex, and Pseudomonas fuscovaginae. Causal agents, pathogenicity determinants, interactions among the various pathogens, epidemiology, geographical distribution, and control options will be discussed.
Keywords: Fusarium fujikuroi complex; Pseudomonas fuscovaginae; Sarocladium oryzae; fumonisins; grain discoloration; phytotoxins; rice; sheath rot.
Figures




References
-
- Abbas H. K., Boyette D. C., Hoagland E. R. (1995). Phytotoxicity of Fusarium, other fungal isolates, and of the phytotoxins fumonisin, fusaric acid, and moniliformin to jimsonweed. Phytoprotection 76 17–25. 10.7202/706081ar - DOI
-
- Adorada D. L., Stodart B. J., Cruz C. V., Gregorio G., Pangga I., Ash G. J. (2013). Standardizing resistance screening to Pseudomonas fuscovaginae and evaluation of rice germplasm at seedling and adult plant growth stages. Euphytica 192 1–16. 10.1007/s10681-012-0804-z - DOI
-
- Adorada D. L., Stodart B. J., Pangga I. B., Ash G. J. (2015). Implications of bacterial contaminated seed lots and endophytic colonization by Pseudomonas fuscovaginae on rice establishment. Plant Pathol. 64 43–50. 10.1111/ppa.12243 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

