The Receptor for Activated C Kinase in Plant Signaling: Tale of a Promiscuous Little Molecule
- PMID: 26697044
- PMCID: PMC4672068
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01090
The Receptor for Activated C Kinase in Plant Signaling: Tale of a Promiscuous Little Molecule
Abstract
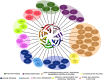
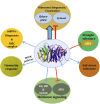
Two decades after the first report of the plant homolog of the Receptor for Activated C Kinase 1 (RACK1) in cultured tobacco BY2 cells, a significant advancement has been made in the elucidation of its cellular and molecular role. The protein is now implicated in many biological functions including protein translation, multiple hormonal responses, developmental processes, pathogen infection resistance, environmental stress responses, and miRNA production. Such multiple functional roles are consistent with the scaffolding nature of the plant RACK1 protein. A significant advance was achieved when the β-propeller structure of the Arabidopsis RACK1A isoform was elucidated, thus revealing that its conserved seven WD repeats also assembled into this typical topology. From its crystal structure, it became apparent that it shares the structural platform for the interaction with ligands identified in other systems such as mammals. Although RACK1 proteins maintain conserved Protein Kinase C binding sites, the lack of a bona fide PKC adds complexity and enigma to the nature of the ligand partners with which RACK1 interacts in plants. Nevertheless, ligands recently identified using the split-ubiquitin based and conventional yeast two-hybrid assays, have revealed that plant RACK1 is involved in several processes that include defense response, drought and salt stress, ribosomal function, cell wall biogenesis, and photosynthesis. The information acquired indicates that, in spite of the high degree of conservation of its structure, the functions of the plant RACK1 homolog appear to be distinct and diverse from those in yeast, mammals, insects, etc. In this review, we take a critical look at the novel information regarding the many functions in which plant RACK1 has been reported to participate, with a special emphasis on the information on its currently identified and missing ligand partners.
Keywords: RACK1; WD-repeat protein; WD40 domain; hormonal regulation; signal transduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tyrosine Phosphorylation Based Homo-dimerization of Arabidopsis RACK1A Proteins Regulates Oxidative Stress Signaling Pathways in Yeast.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Feb 24;7:176. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00176. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 26941753 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of a signal transduction regulator, RACK1, from Arabidopsis thaliana.Protein Sci. 2008 Oct;17(10):1771-80. doi: 10.1110/ps.035121.108. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Protein Sci. 2008. PMID: 18715992 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis scaffold protein RACK1A interacts with diverse environmental stress and photosynthesis related proteins.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 May;8(5):e24012. doi: 10.4161/psb.24012. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23435172 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of ribosomal RACK1 and its role in translational control.Cell Signal. 2017 Jul;35:272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.01.026. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cell Signal. 2017. PMID: 28161490 Review.
-
RACK1 regulates neural development.Neural Regen Res. 2017 Jul;12(7):1036-1039. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.211175. Neural Regen Res. 2017. PMID: 28852378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic Review of Plant Ribosome Heterogeneity and Specialization.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Jun 25;11:948. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00948. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32670337 Free PMC article.
-
The composition and turnover of the Arabidopsis thaliana 80S cytosolic ribosome.Biochem J. 2020 Aug 28;477(16):3019-3032. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200385. Biochem J. 2020. PMID: 32744327 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Subcellular Localization of Host Proteins Induced by Plant Viruses.Viruses. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):677. doi: 10.3390/v13040677. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33920930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Proteins Related to Defense Responses in Arabidopsis Plants Transformed with the rolB Oncogene.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 18;24(3):1880. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031880. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768198 Free PMC article.
-
Time-resolved interaction proteomics of the GIGANTEA protein under diurnal cycles in Arabidopsis.FEBS Lett. 2019 Feb;593(3):319-338. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13311. Epub 2018 Dec 28. FEBS Lett. 2019. PMID: 30536871 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

