Mendelizing all Components of a Pyramid of Three Yield QTL in Tomato
- PMID: 26697048
- PMCID: PMC4678209
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.01096
Mendelizing all Components of a Pyramid of Three Yield QTL in Tomato
Abstract
Molecular markers allowed breeders to mendelize quantitative trait loci (QTL) providing another demonstration that quantitative traits are governed by the same principles as single qualitative genes. This research extends the QTL analysis to two and three QTL and tests our ability to mendelize an oligogenic trait. In tomato, agricultural yield is determined by the weight of the fruits harvested per unit area and the total soluble solids (% Brix)-sugars and acids. The current study explores the segregation of multiple independent yield-related QTL that were identified and mapped using introgression lines (IL) of Solanum pennellii in cultivated processing tomato (S. lycopersicum). We screened 45 different double and triple IL-QTL combinations for agricultural yield, to identify QTL pyramids that behaved in an additive manner and were suitable substrate for mendelizing an oligogenic trait. A pyramid of three independent QTL that significantly improved Brix(∗)Yield (BXY - the soluble solids output per unit area) compared to M82 was selected. In the progenies of the tri-hybrid we bred using markers a nearly isogenic 'immortalized F2.' While the common mode of QTL-QTL interactions across the 45 IL-QTLs combinations was less than additive, the three QTLs in the selected triple-stack performed in an additive manner which made it an exceptional material for breeding. This study demonstrates that using the phenotypic effect of all 27 possible QTL-alleles combinations it is possible to make reliable predictions about the genotypes that will maximize the yield.
Keywords: QTL; epistasis; mendelizing; tomato; wild species; yield.
Figures
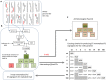

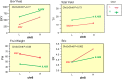

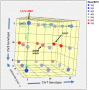
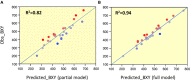

References
-
- Bateson W. (1909). Mendel’s Principles of Heredity. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
- Bernatzky R., Tanksley S. D. (1986). Methods for detection of single or low copy sequences in tomato on southern blots. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 4 37–41. 10.1007/BF02672487 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

