Transfection of microRNA Mimics Should Be Used with Caution
- PMID: 26697058
- PMCID: PMC4667072
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00340
Transfection of microRNA Mimics Should Be Used with Caution
Abstract
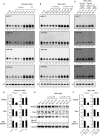
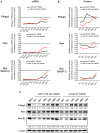
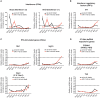
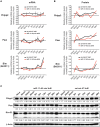
Transient transfection of chemically synthesized microRNA (miRNA) mimics is being used extensively to study the functions and mechanisms of endogenous miRNAs. However, it remains unclear whether transfected miRNAs behave similarly to endogenous miRNAs. Here we show that transient transfection of miRNA mimics into HeLa cells by a commonly used method led to the accumulation of high molecular weight RNA species and a few hundred fold increase in mature miRNA levels. In contrast, expression of the same miRNAs through lentiviral infection or plasmid transfection of HeLa cells, transgenic expression in primary lymphocytes, and endogenous overexpression in lymphoma and leukemia cell lines did not lead to the appearance of high molecular weight RNA species. The increase of mature miRNA levels in these cells was below 10-fold, which was sufficient to suppress target gene expression and to drive lymphoma development in mice. Moreover, transient transfection of miRNA mimics at high concentrations caused non-specific alterations in gene expression, while at low concentrations achieved expression levels comparable to other methods but failed to efficiently suppress target gene expression. Small RNA deep sequencing analysis revealed that the guide strands of miRNA mimics were frequently mutated, while unnatural passenger strands of some miRNA mimics accumulated to high levels. The high molecular weight RNA species were a heterogeneous mixture of several classes of RNA species generated by concatemerization, 5'- and 3'-end tailing of miRNA mimics. We speculate that the supraphysiological levels of mature miRNAs and these artifactual RNA species led to non-specific changes in gene expression. Our results have important implications for the design and interpretation of experiments primarily employing transient transfection of miRNA mimics.
Keywords: guide strand mutation; high molecular weight RNA species; miR-155; miR-17~92; microRNA mimics; transient transfection; unnatural passenger strand.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peritoneal fluid modifies the microRNA expression profile in endometrial and endometriotic cells from women with endometriosis.Hum Reprod. 2015 Oct;30(10):2292-302. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev204. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Hum Reprod. 2015. PMID: 26307093
-
Passenger strand loading in overexpression experiments using microRNA mimics.RNA Biol. 2015;12(8):787-91. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1020270. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26121563 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of a microRNA expression vector for function analysis of microRNA.J Control Release. 2011 Feb 28;150(1):94-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.12.001. Epub 2010 Dec 10. J Control Release. 2011. PMID: 21146569
-
On measuring miRNAs after transient transfection of mimics or antisense inhibitors.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55214. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055214. Epub 2013 Jan 24. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23358900 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing-based microRNA expression signatures in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: dual strands of pre-miR-150 as antitumor miRNAs.Oncotarget. 2017 May 2;8(18):30288-30304. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16327. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415821 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Renal miR-148b is associated with megalin down-regulation in IgA nephropathy.Biosci Rep. 2018 Nov 13;38(6):BSR20181578. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181578. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30355654 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34a deficiency leads to impaired wound closure by augmented inflammation in mice.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Apr;8(7):447. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.161. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32395491 Free PMC article.
-
The Interaction between microRNAs and the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 13;22(18):9887. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189887. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Re-evaluating Strategies to Define the Immunoregulatory Roles of miRNAs.Trends Immunol. 2017 Aug;38(8):558-566. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Trends Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28666937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-212/ABCG2-axis contributes to development of imatinib-resistance in leukemic cells.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 26;8(54):92018-92031. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21272. eCollection 2017 Nov 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29190894 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

