Luoyutong Treatment Promotes Functional Recovery and Neuronal Plasticity after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats
- PMID: 26697095
- PMCID: PMC4678236
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/369021
Luoyutong Treatment Promotes Functional Recovery and Neuronal Plasticity after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats
Abstract
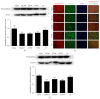
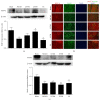
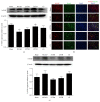
Luoyutong (LYT) capsule has been used to treat cerebrovascular diseases clinically in China and is now patented and approved by the State Food and Drug Administration. In this retrospective validation study we investigated the ability of LYT to protect against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion followed by reperfusion. Capsule containing LYT (high dose and medium dose) as treatment group and Citicoline Sodium as positive control treatment group were administered daily to rats 30 min after reperfusion. Treatment was continued for either 3 days or 14 days. A saline solution was administered to control animals. Behavior tests were performed after 3 and 14 days of treatment. Our findings revealed that LYT treatment improved the neurological outcome, decreased cerebral infarction volume, and reduced apoptosis. Additionally, LYT improved neural plasticity, as the expression of synaptophysin, microtubule associated protein, and myelin basic protein was upregulated by LYT treatment, while neurofilament 200 expression was reduced. Moreover, levels of brain derived neurotrophic factor and basic fibroblast growth factor were increased. Our results suggest that LYT treatment may protect against ischemic injury and improve neural plasticity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Combined nimodipine and citicoline reduce infarct size, attenuate apoptosis and increase bcl-2 expression after focal cerebral ischemia.Neuroscience. 2003;118(1):107-13. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00912-0. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12676142
-
Neuroprotection, learning and memory improvement of a standardized extract from Renshen Shouwu against neuronal injury and vascular dementia in rats with brain ischemia.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 May 13;165:118-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.027. Epub 2015 Feb 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25704930
-
Protective effect of Danhong Injection combined with Naoxintong Capsule on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;211:348-357. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Oct 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28986333
-
PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to neuroprotective effect of Tongxinluo against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 2;181:8-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.028. Epub 2016 Jan 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26805466
-
Effects of Noggin-Transfected Neural Stem Cells on Neural Functional Recovery and Underlying Mechanism in Rats with Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017 Jul;26(7):1547-1559. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.02.034. Epub 2017 May 3. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017. PMID: 28478981
Cited by
-
Ginkgolide B promotes the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, both in vivo and in vitro.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Jul;13(7):1204-1211. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.232476. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30028328 Free PMC article.
-
[Protective effect of histone acetylation against cortical injury in neonatal rats].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jan;19(1):81-87. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2017.01.014. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28100329 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of a Novel Inhibitor of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase in the Rat Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia.Cells. 2020 Aug 8;9(8):1860. doi: 10.3390/cells9081860. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32784475 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of a New C-Jun N-terminal Kinase Inhibitor in the Model of Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rats.Molecules. 2019 May 3;24(9):1722. doi: 10.3390/molecules24091722. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31058815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun K., Hu Q., Zhou C. M., et al. Cerebralcare Granule, a Chinese herb compound preparation, improves cerebral microcirculatory disorder and hippocampal CA1 neuron injury in gerbils after ischemia-reperfusion. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2010;130(2):398–406. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.05.030. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

