Mechanism of lignin inhibition of enzymatic biomass deconstruction
- PMID: 26697106
- PMCID: PMC4687093
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-015-0379-8
Mechanism of lignin inhibition of enzymatic biomass deconstruction
Abstract
Background: The conversion of plant biomass to ethanol via enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis offers a potentially sustainable route to biofuel production. However, the inhibition of enzymatic activity in pretreated biomass by lignin severely limits the efficiency of this process.
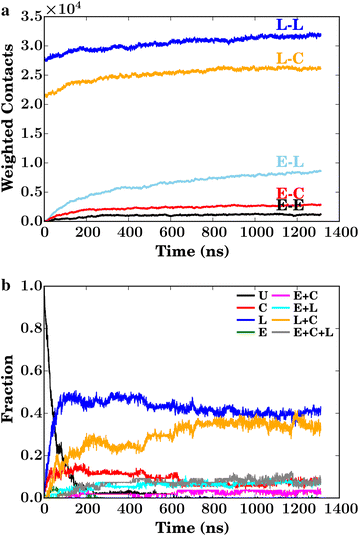
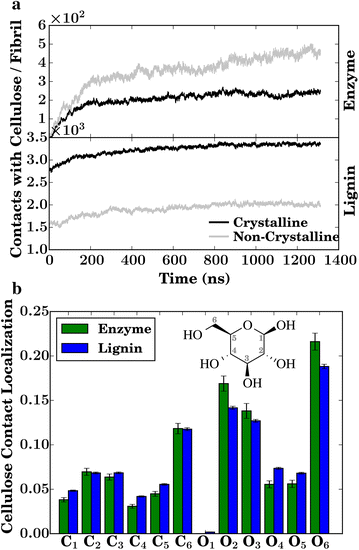
Results: By performing atomic-detail molecular dynamics simulation of a biomass model containing cellulose, lignin, and cellulases (TrCel7A), we elucidate detailed lignin inhibition mechanisms. We find that lignin binds preferentially both to the elements of cellulose to which the cellulases also preferentially bind (the hydrophobic faces) and also to the specific residues on the cellulose-binding module of the cellulase that are critical for cellulose binding of TrCel7A (Y466, Y492, and Y493).
Conclusions: Lignin thus binds exactly where for industrial purposes it is least desired, providing a simple explanation of why hydrolysis yields increase with lignin removal.
Keywords: Biofuel; Cel7A; Cellulose crystallinity; Lignin.
Figures







References
-
- Jorgensen H, Kristensen JB, Felby C. Enzymatic conversion of lignocellulose into fermentable sugars: challenges and opportunities. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin. 2007;1(2):119–134. doi: 10.1002/bbb.4. - DOI
-
- Yang B, Wyman CE. Pretreatment: the key to unlocking low-cost cellulosic ethanol. Biofuel Bioprod Biorefining. 2008;2(1):26–40. doi: 10.1002/bbb.49. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

