New digital tool to facilitate subcutaneous insulin therapy orders: an inpatient insulin dose calculator
- PMID: 26697118
- PMCID: PMC4687348
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-015-0111-7
New digital tool to facilitate subcutaneous insulin therapy orders: an inpatient insulin dose calculator
Abstract
Background: Inpatient hyperglycemia is associated with adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients, with or without known diabetes. The adherence to American College of Endocrinology and American Diabetes Association guidelines recommendations for inpatient glycemic control is still poor, probably because of their complexity and fear of hypoglycemia.
Objective: To create software system that can assist health care providers and hospitalists to manage the insulin therapy orders and turn them into a less complicated issue.
Methods: A software system was idealized and developed, according to recommendations of major consensus and medical literature.
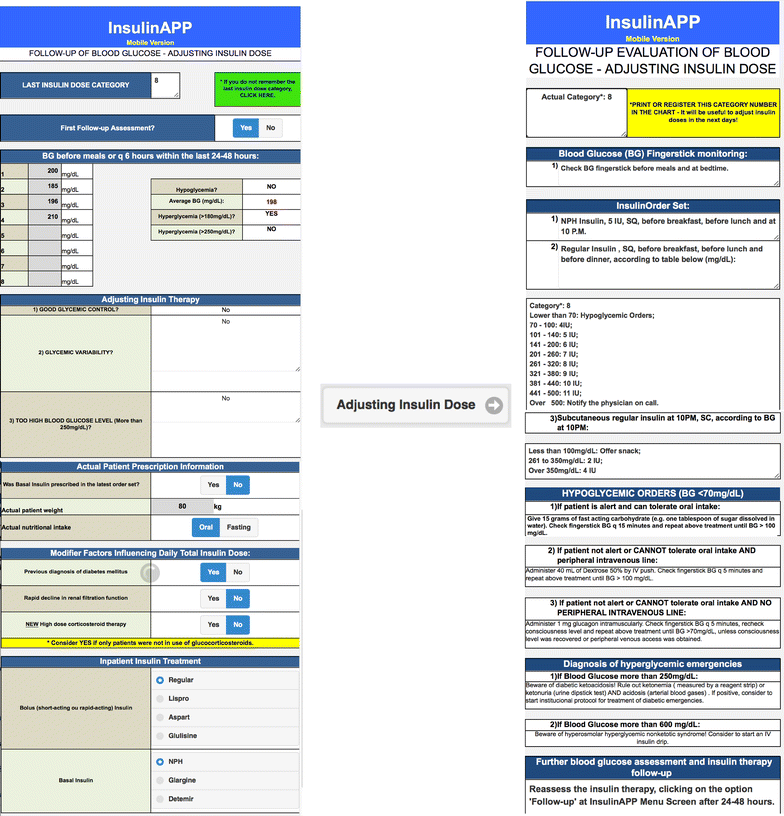
Results: HTML software was developed to be readily accessed from a workstation, tablet or smartphone. Standard initial daily total dose of insulin was 0.4 units/kg and could be modified by distinct factors, such as chronological age, renal and liver function, and high dose corticosteroids use. Insulin therapy consisted of basal, prandial and correction insulin according to nutritional support, glycemic control and outpatient treatment for diabetes. Human insulin or insulin analogues could be options for insulin therapy. Sensitivity factor was based on 1800 Rule for rapid-acting insulin and the 1500 Rule for short-acting insulin. Insulin-naïve patients with initial BG level less than 250 mg/dL were considered to have an initial step-wise approach with prandial and correction insulin. The calculator system has allowed insulin dose readjustments periodically, according to daily average blood glucose measurements.
Conclusion: We developed software that can be a useful tool for all public hospitals, where generally human insulin is the only available.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Hospitalization; Hyperglycemia; Insulin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Addressing hyperglycemia from hospital admission to discharge.Curr Med Res Opin. 2010 Mar;26(3):589-98. doi: 10.1185/03007990903566822. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010. PMID: 20078323 Review.
-
Hyperglycemia management in the hospital setting.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007 May 15;64(10 Suppl 6):S9-S14. doi: 10.2146/ajhp070102. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17494893
-
Reexamining the evidence for inpatient glucose control: new recommendations for glycemic targets.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010 Aug;67(16 Suppl 8):S3-8. doi: 10.2146/ajhp100171. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20689151 Review.
-
Practical implications of the revised guidelines for inpatient glycemic control.Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2009 Dec;119(12):801-9. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2009. PMID: 20010466 Review.
-
Improving glycemic control in medical inpatients: a pilot study.J Hosp Med. 2008 Jan;3(1):55-63. doi: 10.1002/jhm.263. J Hosp Med. 2008. PMID: 18257047
Cited by
-
Electronic Glycemic Management System Improved Glycemic Control and Reduced Complications in Patients With Diabetes Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024 Aug 3:19322968241268352. doi: 10.1177/19322968241268352. Online ahead of print. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39096188 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of DPP4 Inhibitor in Platelet Reactivity and Other Cardiac Risk Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Myocardial Infarction.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 29;11(19):5776. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195776. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233642 Free PMC article.
-
3rd Guideline for Perioperative Cardiovascular Evaluation of the Brazilian Society of Cardiology.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2017 Jan-Feb;109(3 Supl 1):1-104. doi: 10.5935/abc.20170140. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 29044300 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A decade of InsulinAPP: validation using COSMIN and clinical advancements since its initial publication.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 May 10;17(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01717-5. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40349072 Free PMC article.
-
InsulinAPP application protocol for the inpatient management of type 2 diabetes on a hospitalist-managed ward: a retrospective study.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Sept 08;66(4):498-505. doi: 10.20945/2359-3997000000496. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35758838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Magaji V, Johnston JM. Inpatient management of hyperglycemia and diabetes. Clinical Diabetes. 2011;29(1):3–9. doi: 10.2337/diaclin.29.1.3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

