Inhibition of NA(+)/H(+) Exchanger 1 Attenuates Renal Dysfunction Induced by Advanced Glycation End Products in Rats
- PMID: 26697498
- PMCID: PMC4677205
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1802036
Inhibition of NA(+)/H(+) Exchanger 1 Attenuates Renal Dysfunction Induced by Advanced Glycation End Products in Rats
Abstract
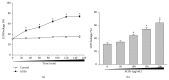
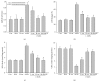
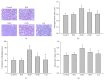
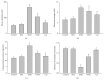
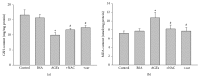
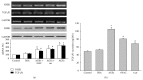
It has been recognized that sodium hydrogen exchanger 1 (NHE1) is involved in the development of diabetic nephropathy. The role of NHE1 in kidney dysfunction induced by advanced glycation end products (AGEs) remains unknown. Renal damage was induced by AGEs via tail vein injections in rats. Function and morphology of kidney were determined. Compared to vehicle- or BSA-treated rats, AGEs caused abnormalities of kidney structures and functions in rats, accompanied with higher MDA level and lower GSH content. Gene expressions of NHE1 gene and TGF-β1 in the renal cortex and urine were also increased in AGEs-injected rats. Importantly, all these detrimental effects induced by AGEs were reversed by inhibition of NHE1 or suppression of oxidative stress. These pieces of data demonstrated that AGEs may activate NHE1 to induce renal damage, which is related to TGF-β1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative Stress-Activated NHE1 Is Involved in High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells.Yonsei Med J. 2016 Sep;57(5):1252-9. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.5.1252. Yonsei Med J. 2016. PMID: 27401659 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt1 resists advanced glycation end products-induced expressions of fibronectin and TGF-β1 by activating the Nrf2/ARE pathway in glomerular mesangial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:528-540. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.029. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23891678
-
Involvement of Na+/H+ exchanger 1 in advanced glycation end products-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 Oct 24;375(3):384-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.008. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. PMID: 18703017
-
[The protective effect of exenatide on the renal injury in diabetic rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Feb 8;33(2):128-131. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5466.2017.033. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29931919 Chinese.
-
Advanced glycation end products in kidney transplant patients: a putative role in the development of chronic renal transplant dysfunction.Am J Kidney Dis. 2004 Jun;43(6):966-75. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2004.02.008. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004. PMID: 15168376 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress-Activated NHE1 Is Involved in High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells.Yonsei Med J. 2016 Sep;57(5):1252-9. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.5.1252. Yonsei Med J. 2016. PMID: 27401659 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of Na/H exchanger stimulates glioma tumor immunogenicity and enhances combinatorial TMZ and anti-PD-1 therapy.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 27;9(10):1010. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1062-3. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30262908 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia via activation of thromboxane A2 receptor impairs the integrity and function of blood-brain barrier in microvascular endothelial cells.Oncotarget. 2017 May 2;8(18):30030-30038. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16273. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28415790 Free PMC article.
-
AGE-RAGE interaction in the TGFβ2-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition of human lens epithelial cells.Glycoconj J. 2016 Aug;33(4):631-43. doi: 10.1007/s10719-016-9686-y. Epub 2016 Jun 4. Glycoconj J. 2016. PMID: 27263094 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin reduces high glucose-induced oxidative stress and miR-21-dependent TRAF3IP2 induction and RECK suppression, and inhibits human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Cell Signal. 2020 Apr;68:109506. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109506. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 31862399 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

