TORn about SASP regulation
- PMID: 26697828
- PMCID: PMC4825754
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1105694
TORn about SASP regulation
Keywords: MAPKAPK2; SASP; Senescence; ZFP36L1; aging; cancer; mTOR; oncogene-induced senescence; senescence-associated secretory phenotype.
Figures
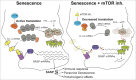
Comment on
- doi: 10.1038/ncb3225
Similar articles
-
mTOR regulates MAPKAPK2 translation to control the senescence-associated secretory phenotype.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Sep;17(9):1205-17. doi: 10.1038/ncb3225. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26280535 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR favors senescence over quiescence in p53-arrested cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2010 Jun;2(6):327-8. doi: 10.18632/aging.100164. Aging (Albany NY). 2010. PMID: 20603524 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Decision-making by p53 and mTOR.Aging (Albany NY). 2010 Jun;2(6):324-6. doi: 10.18632/aging.100166. Aging (Albany NY). 2010. PMID: 20603526 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rapamycin and the inhibition of the secretory phenotype.Exp Gerontol. 2017 Aug;94:89-92. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2017.01.026. Epub 2017 Feb 4. Exp Gerontol. 2017. PMID: 28167236 Review.
-
Targeting the SASP to combat ageing: Mitochondria as possible intracellular allies?Bioessays. 2017 May;39(5). doi: 10.1002/bies.201600235. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Bioessays. 2017. PMID: 28217839 Review.
Cited by
-
The Immortal Senescence.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1534:1-15. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6670-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27812863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiobiological effects of wound fluid on breast cancer cell lines and human-derived tumor spheroids in 2D and microfluidic culture.Sci Rep. 2022 May 10;12(1):7668. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11023-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35538133 Free PMC article.
-
Postbiotics as Molecules Targeting Cellular Events of Aging Brain-The Role in Pathogenesis, Prophylaxis and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Nutrients. 2024 Jul 12;16(14):2244. doi: 10.3390/nu16142244. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39064687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals distinct senotypes and a quiescence-senescence continuum at the transcriptome level following chemotherapy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 14:2025.05.13.653730. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.13.653730. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40463227 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Network pharmacology and RNA-sequencing reveal the molecular mechanism of Xuebijing injection on COVID-19-induced cardiac dysfunction.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Apr;131:104293. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104293. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33662681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Narita M, et al.. Science 2011; 332:966-70; PMID:21512002; http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1205407 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iglesias-Bartolome R, et al. Cell Stem Cell 2012; 11:401-14; PMID:22958932; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2012.06.007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Laberge RM, et al.. Nat Cell Biol 2015; 17:1049-61; PMID:26147250; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb3195 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herranz N, et al.. Nat Cell Biol 2015; 17:1205-17; PMID:26280535; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb3225 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thoreen CC, et al. Nature 2012; 485:109-13; PMID:22552098; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11083 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
