Skp2 is required for Aurora B activation in cell mitosis and spindle checkpoint
- PMID: 26697838
- PMCID: PMC4825700
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1120916
Skp2 is required for Aurora B activation in cell mitosis and spindle checkpoint
Abstract
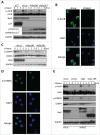
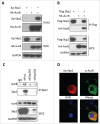
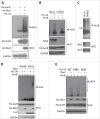
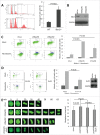
The Aurora B kinase plays a critical role in cell mitosis and spindle checkpoint. Here, we showed that the ubiquitin E3-ligase protein Skp2, also as a cell-cycle regulatory protein, was required for the activation of Aurora B and its downstream protein. When we restored Skp2 knockdown Hela cells with Skp2 and Skp2-LRR E3 ligase dead mutant we found that Skp2 could rescue the defect in the activation of Aurora B, but the mutant failed to do so. Furthermore, we discovered that Skp2 could interact with Aurora B and trigger Aurora B Lysine (K) 63-linked ubiquitination. Finally, we demonstrated the essential role of Skp2 in cell mitosis progression and spindle checkpoint, which was Aurora B dependent. Our results identified a novel ubiquitinated substrate of Skp2, and also indicated that Aurora B ubiquitination might serve as an important event for Aurora B activation in cell mitosis and spindle checkpoint.
Keywords: Aurora B; Skp2; cell mitosis; genomic stability; spindle checkpoint; tumorigenesis; ubiquitination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bub1 and aurora B cooperate to maintain BubR1-mediated inhibition of APC/CCdc20.J Cell Sci. 2005 Aug 15;118(Pt 16):3639-52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02487. Epub 2005 Jul 26. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16046481
-
Regulation of Skp2 levels by the Pim-1 protein kinase.J Biol Chem. 2010 Sep 17;285(38):29128-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.137240. Epub 2010 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20663873 Free PMC article.
-
Deubiquitinase USP35 as a novel mitotic regulator via maintenance of Aurora B stability.BMB Rep. 2018 Jun;51(6):261-262. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2018.51.6.110. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 29764563 Free PMC article.
-
Control of DNA synthesis and mitosis by the Skp2-p27-Cdk1/2 axis.Mol Cell. 2004 May 21;14(4):414-6. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00268-0. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15149588 Review.
-
A role for Cdc48/p97 and Aurora B in controlling chromatin condensation during exit from mitosis.Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Feb;88(1):23-8. doi: 10.1139/o09-119. Biochem Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20130676 Review.
Cited by
-
CACYBP Enhances Cytoplasmic Retention of P27Kip1 to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression in the Absence of RNF41 Mediated Degradation.Theranostics. 2019 Oct 22;9(26):8392-8408. doi: 10.7150/thno.36838. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31754404 Free PMC article.
-
Skp2 is over-expressed in breast cancer and promotes breast cancer cell proliferation.Cell Cycle. 2016 May 18;15(10):1344-51. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1160986. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27111245 Free PMC article.
-
Genotoxicity-Stimulated and CYLD-Driven Malignant Transformation.Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Aug 5;14:2339-2356. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S373557. eCollection 2022. Cancer Manag Res. 2022. PMID: 35958947 Free PMC article.
-
Skp2-mediated MLKL degradation confers cisplatin-resistant in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Commun Biol. 2023 Aug 2;6(1):805. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05166-6. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37532777 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of SKP2 in Cancer Drug Resistance.Cells. 2021 May 10;10(5):1147. doi: 10.3390/cells10051147. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34068643 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ditchfield C, Johnson VL, Tighe A, Ellston R, Haworth C, Johnson T, Mortlock A, Keen N, Taylor SS. Aurora B couples chromosome alignment with anaphase by targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to kinetochores. J Cell Biol 2003; 161:267-80; PMID:12719470; http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200208091 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C, Schnapp G, Walter R, Heckel A, van Meel J, Rieder CL, Peters JM. The small molecule Hesperadin reveals a role for Aurora B in correcting kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol 2003; 161:281-94; PMID:12707311; http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200208092 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sumara I, Quadroni M, Frei C, Olma MH, Sumara G, Ricci R, Peter M. A Cul3-based E3 ligase removes Aurora B from mitotic chromosomes, regulating mitotic progression and completion of cytokinesis in human cells. Dev Cell 2007; 12:887-900; PMID:17543862; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2007.03.019 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frescas D, Pagano M. Deregulated proteolysis by the F-box proteins SKP2 and β-TrCP: tipping the scales of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8:438-49; PMID:18500245; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc2396 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lin HK, Wang G, Chen Z, Teruya-Feldstein J, Liu Y, Chan CH, Yang WL, Erdjument-Bromage H, Nakayama KI, Nimer S, et al.. Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cytosolic localization and oncogenic function of Skp2 by Akt/PKB. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11:420-32; PMID:19270694; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb1849 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
