p27Kip1 inhibits the cell cycle through non-canonical G1/S phase-specific gatekeeper mechanism
- PMID: 26697844
- PMCID: PMC4825794
- DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1100775
p27Kip1 inhibits the cell cycle through non-canonical G1/S phase-specific gatekeeper mechanism
Abstract
The cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor p27Kip1 has been shown to regulate cellular proliferation via inhibition of CDK activities. It is now recognized that p27Kip1 can regulate cellular processes through non-canonical, CDK-independent mechanisms. We have developed an inducible p27Kip1 model in cultured cells to explore CDK-independent p27Kip1 regulation of biological processes. We present evidence that p27Kip1 can function in a CDK-independent manner to inhibit entry and/or progression of S phase. Even though this p27Kip1 mechanism is non-canonical it does requires the intact cyclin-binding motif in p27Kip1. We suggest a mechanism similar to that proposed in post-mitotic neural cells whereby p27Kip1 functions to coordinate growth arrest and apoptosis. Our hypothesis supports the concept that p27Kip1 is a gatekeeper for the entry and progression of S phase through interaction with specific protein(s) or via binding to specific DNA sequences in a CDK-independent manner.
Keywords: cell cycle; cyclin F; cyclin-dependent kinases; non-canonical; p27Kip1.
Figures

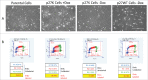
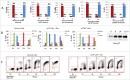
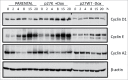
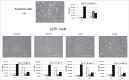


Similar articles
-
The non-canonical functions of p27(Kip1) in normal and tumor biology.Cell Cycle. 2016 May 2;15(9):1189-201. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1157238. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27082696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progression of LNCaP prostate tumor cells during androgen deprivation: hormone-independent growth, repression of proliferation by androgen, and role for p27Kip1 in androgen-induced cell cycle arrest.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Jul;12(7):941-53. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.7.0136. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9658399
-
Involvement of p27Kip1 in G1 arrest by high dose 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells.Oncogene. 2000 Feb 3;19(5):670-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203369. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10698512
-
TGF-beta mediated G1 arrest in a human melanoma cell line lacking p15INK4B: evidence for cooperation between p21Cip1/WAF1 and p27Kip1.Oncogene. 1996 Dec 5;13(11):2447-57. Oncogene. 1996. PMID: 8957087
-
HER2-targeting antibodies modulate the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 via multiple signaling pathways.Cell Cycle. 2005 Jan;4(1):87-95. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.1.1360. Epub 2005 Jan 10. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 15611642 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of paclitaxel intervention on pulmonary vascular remodeling in rats with pulmonary hypertension.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Feb;17(2):1163-1170. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7045. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30679989 Free PMC article.
-
The non-canonical functions of p27(Kip1) in normal and tumor biology.Cell Cycle. 2016 May 2;15(9):1189-201. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1157238. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27082696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sumoylation in p27kip1 via RanBP2 promotes cancer cell growth in cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939.BMC Mol Biol. 2017 Sep 7;18(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12867-017-0100-5. BMC Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28882106 Free PMC article.
-
p27kip1 Modulates the Morphology and Phagocytic Activity of Microglia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 9;23(18):10432. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810432. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142366 Free PMC article.
-
Possibility of inducing tumor cell senescence during therapy.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jul;22(1):496. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12757. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33981358 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 1995; 9:1149-63; PMID:7758941; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.9.10.1149 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roberts JM, Koff A, Polyak K, Firpo E, Collins S, Ohtsubo M, Massague J. Cyclins, Cdks, and cyclin kinase inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 1994; 59:31-8; PMID:7587083; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/SQB.1994.059.01.006 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 1999; 13:1501-12; PMID:10385618; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.12.1501 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hengst L, Dulic V, Slingerland JM, Lees E, Reed SI. A cell cycle-regulated inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994; 91:5291-5; PMID:8202483; http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.12.5291 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon MJ, Sherr CJ, Massague J, Roberts JM, Koff A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-β and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev 1994; 8:9-22; PMID:8288131; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.8.1.9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
