Memantine Attenuates Alzheimer's Disease-Like Pathology and Cognitive Impairment
- PMID: 26697860
- PMCID: PMC4689401
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145441
Memantine Attenuates Alzheimer's Disease-Like Pathology and Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
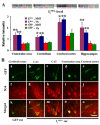
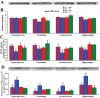
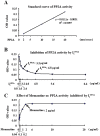
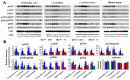
Deficiency of protein phosphatase-2A is a key event in Alzheimer's disease. An endogenous inhibitor of protein phosphatase-2A, inhibitor-1, I1PP2A, which inhibits the phosphatase activity by interacting with its catalytic subunit protein phosphatase-2Ac, is known to be upregulated in Alzheimer's disease brain. In the present study, we overexpressed I1PP2A by intracerebroventricular injection with adeno-associated virus vector-1-I1PP2A in Wistar rats. The I1PP2A rats showed a decrease in brain protein phosphatase-2A activity, abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau, neurodegeneration, an increase in the level of activated glycogen synthase kinase-3beta, enhanced expression of intraneuronal amyloid-beta and spatial reference memory deficit; littermates treated identically but with vector only, i.e., adeno-associated virus vector-1-enhanced GFP, served as a control. Treatment with memantine, a noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist which is an approved drug for treatment of Alzheimer's disease, rescued protein phosphatase-2A activity by decreasing its demethylation at Leu309 selectively and attenuated Alzheimer's disease-like pathology and cognitive impairment in adeno-associated virus vector-1-I1PP2A rats. These findings provide new clues into the possible mechanism of the beneficial therapeutic effect of memantine in Alzheimer's disease patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Protein Phosphatase-2A (PP2A) by I1PP2A Leads to Hyperphosphorylation of Tau, Neurodegeneration, and Cognitive Impairment in Rats.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;45(2):423-35. doi: 10.3233/JAD-142403. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25589718
-
The carboxy-terminal fragment of inhibitor-2 of protein phosphatase-2A induces Alzheimer disease pathology and cognitive impairment.FASEB J. 2010 Nov;24(11):4420-32. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-158477. Epub 2010 Jul 22. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20651003 Free PMC article.
-
An experimental rat model of sporadic Alzheimer's disease and rescue of cognitive impairment with a neurotrophic peptide.Acta Neuropathol. 2012 Jan;123(1):133-51. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0908-x. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Acta Neuropathol. 2012. PMID: 22083255 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models of the sporadic form of Alzheimer's disease: focus on the disease and not just the lesions.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;37(3):469-74. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130827. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 23948903 Review.
-
[Mémantine (Ebixa): a new therapeutic strategy for the treatment of moderate to severe forms of Alzheimer's disease].Encephale. 2004 Jan-Feb;30(1):69-79. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95418-8. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15029079 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Therapies for Prevention and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:2589276. doi: 10.1155/2016/2589276. Epub 2016 Jul 28. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27547756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Memantine Improves Cognitive Function and Alters Hippocampal and Cortical Proteome in Triple Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Exp Neurobiol. 2019 Jun;28(3):390-403. doi: 10.5607/en.2019.28.3.390. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Exp Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31308798 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Amnesic and Neuroprotective Effects of Fluoroethylnormemantine in a Pharmacological Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021 Feb 15;24(2):142-157. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyaa075. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32977336 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Approach of Anti-Cancer Microtubule Stabilizers Against Tauopathy Associated Dementia: Current Status of Clinical and Preclinical Findings.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2019 Jul 2;3(1):179-218. doi: 10.3233/ADR-190125. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2019. PMID: 31435618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of CK2 mitigates Alzheimer's tau pathology by preventing NR2B synaptic mislocalization.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Mar 4;10(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01331-w. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35246269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Quinlan M, Tung YC, Zaidi MS, Wisniewski HM. Microtubule-associated protein tau. A component of Alzheimer paired helical filaments. J Biol Chem. 1986;261(13):6084–9. . - PubMed
-
- Liu F, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Gong CX. Contributions of protein phosphatases PP1, PP2A, PP2B and PP5 to the regulation of tau phosphorylation. The European journal of neuroscience. 2005;22(8):1942–50. . - PubMed
-
- Gong CX, Shaikh S, Wang JZ, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Phosphatase activity toward abnormally phosphorylated tau: decrease in Alzheimer disease brain. Journal of neurochemistry. 1995;65(2):732–8. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

