Pentosan polysulfate preserves renal microvascular P2X1 receptor reactivity and autoregulatory behavior in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
- PMID: 26697978
- PMCID: PMC4796270
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00110.2015
Pentosan polysulfate preserves renal microvascular P2X1 receptor reactivity and autoregulatory behavior in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats
Abstract
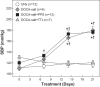
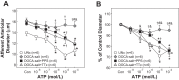
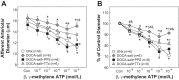
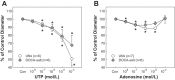
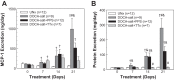
Inflammation contributes to ANG II-associated impairment of renal autoregulation and microvascular P2X1 receptor signaling, but its role in renal autoregulation in mineralocorticoid-induced hypertension is unknown. Autoregulatory behavior was assessed using the blood-perfused juxtamedullary nephron preparation. Hypertension was induced in uninephrectomized control rats (UNx) by subcutaneous implantation of a DOCA pellet plus administration of 1% NaCl in the drinking water (DOCA-salt) for 3 wk. DOCA-salt rats developed hypertension that was unaltered by anti-inflammatory treatment with pentosan polysulfate (DOCA-salt+PPS) but was suppressed with "triple therapy" (hydrochlorothiazide, hydralazine, and reserpine; DOCA-salt+TTx). Baseline arteriolar diameters were similar across all groups. UNx rats exhibited pressure-dependent vasoconstriction with diameters declining to 69 ± 2% of control at 170 mmHg, indicating intact autoregulation. DOCA-salt treatment significantly blunted this pressure-mediated vasoconstriction. Diameters remained between 91 ± 4 and 98 ± 3% of control over 65-170 mmHg, indicating impaired autoregulation. In contrast, pressure-mediated vasoconstriction was preserved in DOCA-salt+PPS and DOCA-salt+TTx rats, reaching 77 ± 7 and 75 ± 3% of control at 170 mmHg, respectively. ATP is required for autoregulation via P2X1 receptor activation. ATP- and β,γ-methylene ATP (P2X1 receptor agonist)-mediated vasoconstriction were markedly attenuated in DOCA-salt rats compared with UNx (P < 0.05), but significantly improved by PPS or TTx (P < 0.05 vs. DOCA-salt) treatment. Arteriolar responses to adenosine and UTP (P2Y2 receptor agonist) were unaffected by DOCA-salt treatment. PPS and TTx significantly reduced MCP-1 and protein excretion in DOCA-salt rats. These results support the hypothesis that hypertension triggers inflammatory cascades but anti-inflammatory treatment preserves renal autoregulation in DOCA-salt rats, most likely by normalizing renal microvascular reactivity to P2X1 receptor activation.
Keywords: afferent arteriole; hypertension; inflammation; purinoceptors; triple therapy.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pentosan polysulfate treatment preserves renal autoregulation in ANG II-infused hypertensive rats via normalization of P2X1 receptor activation.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):F1276-84. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00743.2009. Epub 2010 Mar 3. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20200092 Free PMC article.
-
P2X1 receptor-mediated vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles in angiotensin II-infused hypertensive rats fed a high-salt diet.Hypertension. 2011 Apr;57(4):780-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.168955. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Hypertension. 2011. PMID: 21321307 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosuppression preserves renal autoregulatory function and microvascular P2X(1) receptor reactivity in ANG II-hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013 Mar 15;304(6):F801-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00286.2012. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23269644 Free PMC article.
-
Altered myogenic responsiveness of the renal microvasculature in experimental hypertension.J Hypertens. 1996 Dec;14(12):1387-401. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199612000-00002. J Hypertens. 1996. PMID: 8986920 Review.
-
Renal autoregulation in P2X1 knockout mice.Acta Physiol Scand. 2004 Aug;181(4):445-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201X.2004.01317.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2004. PMID: 15283757 Review.
Cited by
-
Afferent arteriole responsiveness to endothelin receptor activation: does sex matter?Biol Sex Differ. 2019 Jan 3;10(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13293-018-0218-2. Biol Sex Differ. 2019. PMID: 30606254 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of major histocompatibility complex class II invariant chain peptide during chronic lipopolysaccharide treatment rescues autoregulatory behavior.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):F957-F966. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00164.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31432707 Free PMC article.
-
Purinoceptors, renal microvascular function and hypertension.Physiol Res. 2020 Jul 16;69(3):353-369. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934463. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32301620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute toll-like receptor 4 activation impairs rat renal microvascular autoregulatory behaviour.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017 Nov;221(3):204-220. doi: 10.1111/apha.12899. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017. PMID: 28544543 Free PMC article.
-
Purinoceptor: a novel target for hypertension.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Mar;19(1):185-197. doi: 10.1007/s11302-022-09852-8. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 35181831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Blasi ER, Rocha R, Rudolph AE, Blomme EA, Polly ML, McMahon EG. Aldosterone/salt induces renal inflammation and fibrosis in hypertensive rats. Kidney Int 63: 1791–1800, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bobadilla NA, Tack I, Tapia E, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Santamaria J, Jimenez F, Striker LJ, Striker GE, Herrera-Acosta J. Pentosan polysulfate prevents glomerular hypertension and structural injury despite persisting hypertension in 5/6 nephrectomy rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 12: 2080–2087, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Castrop H. Mediators of tubuloglomerular feedback regulation of glomerular filtration: ATP and adenosine. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 189: 3–14, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

