G protein α12 (Gα12) is a negative regulator of kidney injury molecule-1-mediated efferocytosis
- PMID: 26697979
- PMCID: PMC4971893
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00169.2015
G protein α12 (Gα12) is a negative regulator of kidney injury molecule-1-mediated efferocytosis
Abstract
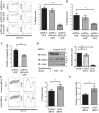
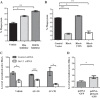
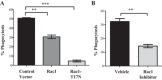
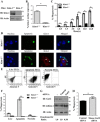
Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) is a receptor for the "eat me" signal, phosphatidylserine, on apoptotic cells. The specific upregulation of KIM-1 by injured tubular epithelial cells (TECs) enables them to clear apoptotic cells (also known as efferocytosis), thereby protecting from acute kidney injury. Recently, we uncovered that KIM-1 binds directly to the α-subunit of heterotrimeric G12 protein (Gα12) and inhibits its activation by reactive oxygen species during renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (Ismail OZ, Zhang X, Wei J, Haig A, Denker BM, Suri RS, Sener A, Gunaratnam L. Am J Pathol 185: 1207-1215, 2015). Here, we investigated the role that Gα12 plays in KIM-1-mediated efferocytosis by TECs. We showed that KIM-1 remains bound to Gα12 and suppresses its activity during phagocytosis. When we silenced Gα12 expression using small interefering RNA, KIM-1-mediated engulfment of apoptotic cells was increased significantly; in contrast overexpression of constitutively active Gα12 (QLGα12) resulted in inhibition of efferocytosis. Inhibition of RhoA, a key effector of Gα12, using a chemical inhibitor or expression of dominant-negative RhoA, had the same effect as inhibition of Gα12 on efferocytosis. Consistent with this, silencing Gα12 suppressed active RhoA in KIM-1-expressing cells. Finally, using primary TECs from Kim-1+/+ and Kim-1-/- mice, we confirmed that engulfment of apoptotic cells requires KIM-1 expression and that silencing Gα12 enhanced efferocytosis by primary TECs. Our data reveal a previously unknown role for Gα12 in regulating efferocytosis and that renal TECs require KIM-1 to mediate this process. These results may have therapeutic implications given the known harmful role of Gα12 in acute kidney injury.
Keywords: G protein; Gα12; kidney; kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1); phagocytosis.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Kidney injury molecule-1 protects against Gα12 activation and tissue damage in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Pathol. 2015 May;185(5):1207-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.02.003. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Am J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25759266 Free PMC article.
-
Tctex-1, a novel interaction partner of Kidney Injury Molecule-1, is required for efferocytosis.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6877-6895. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26578. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29693725 Free PMC article.
-
KIM-1-mediated anti-inflammatory activity is preserved by MUC1 induction in the proximal tubule during ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021 Aug 1;321(2):F135-F148. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00127.2021. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34151589 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotrimeric Gα12/13 proteins in kidney injury and disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;318(3):F660-F672. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00453.2019. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31984793 Review.
-
Kidney injury molecule-1: more than just an injury marker of tubular epithelial cells?J Cell Physiol. 2013 May;228(5):917-24. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24267. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23086807 Review.
Cited by
-
Renocardiac Effects of p-Cresyl Sulfate Administration in Acute Kidney Injury Induced by Unilateral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury In Vivo.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Nov 10;15(11):649. doi: 10.3390/toxins15110649. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999512 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping and functional characterization of murine kidney injury molecule-1 proteolytic cleavage site.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Feb;476(2):1093-1108. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03975-5. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33211259
-
The effects of apoptosis inhibitor of macrophage in kidney diseases.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 4;29(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01597-3. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38178221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the Subtypes of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Based on Pyroptosis-Related Genes.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 1;13(2):275. doi: 10.3390/biom13020275. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830644 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding kidney injury molecule 1: a novel immune factor in kidney pathophysiology.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Mar 15;11(3):1219-1229. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30972157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ajay AK, Kim TM, Ramirez-Gonzalez V, Park PJ, Frank DA, Vaidya VS. A bioinformatics approach identifies signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 and checkpoint kinase 1 as upstream regulators of kidney injury molecule-1 after kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 25: 105–118, 2014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailly V, Zhang Z, Meier W, Cate R, Sanicola M, Bonventre JV. Shedding of kidney injury molecule-1, a putative adhesion protein involved in renal regeneration. J Biol Chem 277: 39739–39748, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Binne LL, Scott ML, Rennert PD. Human TIM-1 associates with the TCR complex and up-regulates T cell activation signals. J Immunol 178: 4342–4350, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

