Anti-inflammatory effects of Hwang-Heuk-San, a traditional Korean herbal formulation, on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages
- PMID: 26698114
- PMCID: PMC4690236
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-015-0971-2
Anti-inflammatory effects of Hwang-Heuk-San, a traditional Korean herbal formulation, on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated murine macrophages
Abstract
Background: Hwang-Heuk-San (HHS), a Korean traditional herbal formula comprising four medicinal herbs, has been used to treat patients with inflammation syndromes and digestive tract cancer for hundreds of years; however, its anti-inflammatory potential is poorly understood. The aim of the present study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of HHS using a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated RAW 264.7 macrophage model.
Methods: The inhibitory effects of HHS on LPS-induced nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) production were examined using Griess reagent and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection kits. The effects of HHS on the expression of inducible NO synthase (iNOS), IL-1β and TNF-α, their upstream signal proteins, including nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), and activator protein (AP-1), were also investigated.
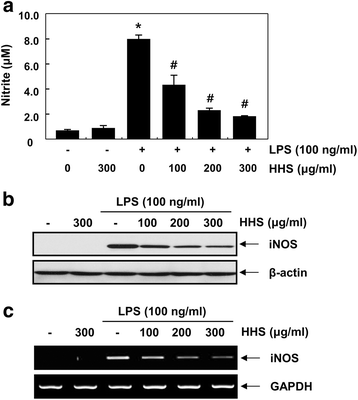
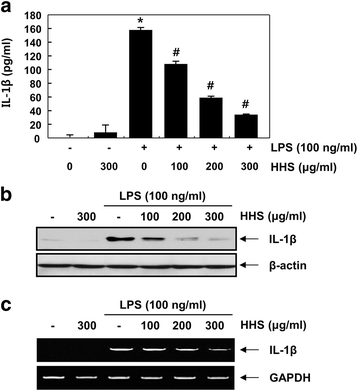
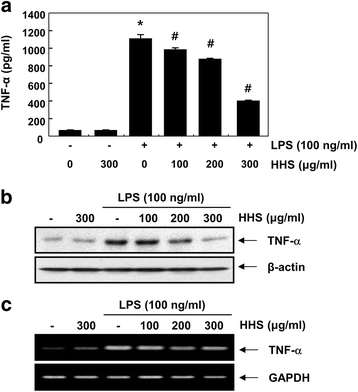
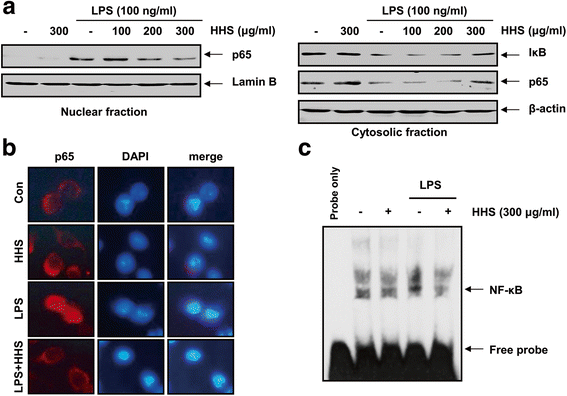
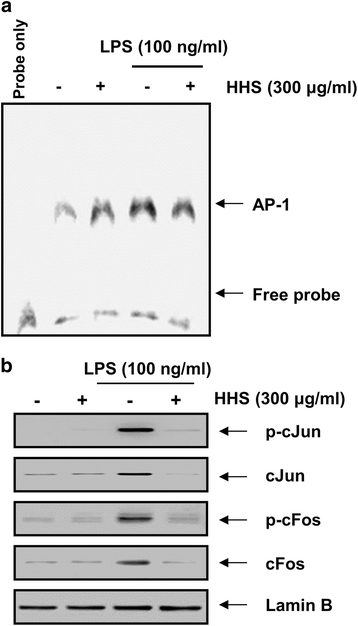
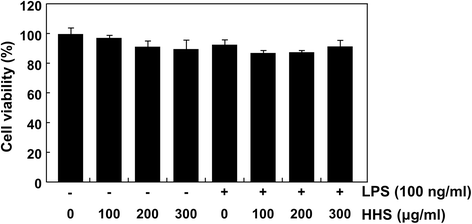
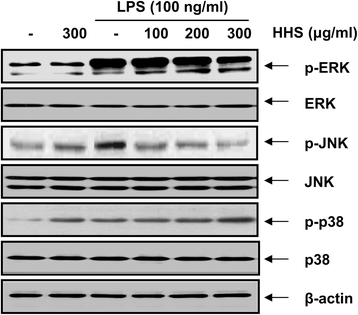
Results: A noncytotoxic concentration of HHS significantly reduced the production of NO, IL-1β and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells, which was correlated with reduced expression of iNOS, IL-1β and TNF-α at the mRNA and protein levels. HHS efficiently blocked the phosphorylation of MAPKs, especially that of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) but not that of the p38 MAPK. The reduced production of inflammatory molecules by HHS was followed by decreased activity of NF-κB and AP-1.
Conclusions: These results suggest that HHS may offer therapeutic potential for treating inflammatory diseases accompanied by macrophage activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cnidilide, an alkylphthalide isolated from the roots of Cnidium officinale, suppresses LPS-induced NO, PGE2, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α production by AP-1 and NF-κB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.021. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27591413
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of the six compounds isolated from Nauclea officinalis Pierrc ex Pitard, and molecular mechanism of strictosamide via suppressing the NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Jan 20;196:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.007. Epub 2016 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27989509
-
Dingchuan tang essential oil inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators via suppressing the IRAK/NF-κB, IRAK/AP-1, and TBK1/IRF3 pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Sep 4;12:2731-2748. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S160645. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30233137 Free PMC article.
-
DXXK exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB/COX-2 signalling pathway and the expression of inflammatory mediators.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 3;178:199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.016. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26571085
-
Exploring the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Australian Native Plants Based on their Ethnopharmacological Knowledge.Chem Biodivers. 2024 Jul;21(7):e202400492. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202400492. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38700281 Review.
Cited by
-
The protective effects of PCPA against monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension are mediated through the downregulation of NFAT-1 and NF-κB.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Jul;40(1):155-163. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3001. Epub 2017 May 26. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28560440 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of lycopene in SW480 human colorectal cancer cells.Nutr Res Pract. 2017 Apr;11(2):90-96. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.2.90. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Nutr Res Pract. 2017. PMID: 28386381 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Symplocos sumuntia Buch.-Ham. Ex D. Don Extract via Blockage of the NF-κB/JNK Signaling Pathways in LPS-Activated Microglial Cells.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 14;11(22):3095. doi: 10.3390/plants11223095. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432823 Free PMC article.
-
Curcuma longa extract reduces serum inflammatory markers and postprandial hyperglycemia in healthy but borderline participants with overweight and glycemia in the normal/prediabetes range: a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial.Front Nutr. 2024 Jan 29;11:1324196. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1324196. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38347961 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Apoptosis and Necrosis Effects of Arctium Lappa Root Extract and Doxorubicin on MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 Cell Lines.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Mar 1;18(3):795-802. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.3.795. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 28441789 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

