Investigation of Congenital Myasthenia Reveals Functional Asymmetry of Invariant Acetylcholine Receptor (AChR) Cys-loop Aspartates
- PMID: 26698174
- PMCID: PMC4751375
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.683995
Investigation of Congenital Myasthenia Reveals Functional Asymmetry of Invariant Acetylcholine Receptor (AChR) Cys-loop Aspartates
Abstract
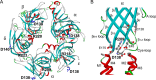
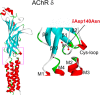
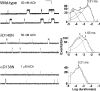
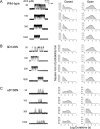
We identify two heteroallelic mutations in the acetylcholine receptor δ-subunit from a patient with severe myasthenic symptoms since birth: a novel δD140N mutation in the signature Cys-loop and a mutation in intron 7 of the δ-subunit gene that disrupts splicing of exon 8. The mutated Asp residue, which determines the disease phenotype, is conserved in all eukaryotic members of the Cys-loop receptor superfamily. Studies of the mutant acetylcholine receptor expressed in HEK 293 cells reveal that δD140N attenuates cell surface expression and apparent channel gating, predicting a reduced magnitude and an accelerated decay of the synaptic response, thus reducing the safety margin for neuromuscular transmission. Substituting Asn for Asp at equivalent positions in the α-, β-, and ϵ-subunits also suppresses apparent channel gating, but the suppression is much greater in the α-subunit. Mutant cycle analysis applied to single and pairwise mutations reveals that αAsp-138 is energetically coupled to αArg-209 in the neighboring pre-M1 domain. Our findings suggest that the conserved αAsp-138 and αArg-209 contribute to a principal pathway that functionally links the ligand binding and pore domains.
Keywords: Cys-loop receptor superfamily; congenital myasthenic syndrome; invariant Cys-loop aspartate; invariant pre-M1 arginine; ion channel; mutant cycle analysis; nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR); patch clamp; receptor structure-function; structure-function.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Karlin A., Holtzman E., Yodh N., Lobel P., Wall J., and Hainfeld J. (1983) The arrangement of the subunits of the acetylcholine receptor of Torpedo californica. J. Biol. Chem. 258, 6678–6681 - PubMed
-
- Lee W. Y., and Sine S. M. (2005) Principal pathway coupling agonist binding to channel gating in nicotinic receptors. Nature 438, 243–247 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

