Analysis of simultaneous MEG and intracranial LFP recordings during Deep Brain Stimulation: a protocol and experimental validation
- PMID: 26698227
- PMCID: PMC4758829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.11.029
Analysis of simultaneous MEG and intracranial LFP recordings during Deep Brain Stimulation: a protocol and experimental validation
Abstract
Background: Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is an effective treatment for several neurological and psychiatric disorders. In order to gain insights into the therapeutic mechanisms of DBS and to advance future therapies a better understanding of the effects of DBS on large-scale brain networks is required.
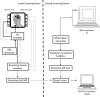
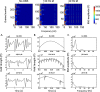
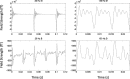
New method: In this paper, we describe an experimental protocol and analysis pipeline for simultaneously performing DBS and intracranial local field potential (LFP) recordings at a target brain region during concurrent magnetoencephalography (MEG) measurement. Firstly we describe a phantom setup that allowed us to precisely characterise the MEG artefacts that occurred during DBS at clinical settings.
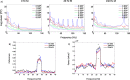
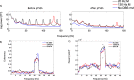
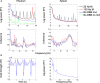
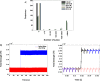
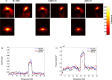
Results: Using the phantom recordings we demonstrate that with MEG beamforming it is possible to recover oscillatory activity synchronised to a reference channel, despite the presence of high amplitude artefacts evoked by DBS. Finally, we highlight the applicability of these methods by illustrating in a single patient with Parkinson's disease (PD), that changes in cortical-subthalamic nucleus coupling can be induced by DBS.
Comparison with existing approaches: To our knowledge this paper provides the first technical description of a recording and analysis pipeline for combining simultaneous cortical recordings using MEG, with intracranial LFP recordings of a target brain nucleus during DBS.
Keywords: Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS); Local Field Potential (LFP); Magnetoencephalography (MEG); Parkinson's disease.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The comparative performance of DBS artefact rejection methods for MEG recordings.Neuroimage. 2020 Oct 1;219:117057. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117057. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32540355 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized beamforming for simultaneous MEG and intracranial local field potential recordings in deep brain stimulation patients.Neuroimage. 2010 May 1;50(4):1578-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.12.115. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20056156 Free PMC article.
-
Rejecting deep brain stimulation artefacts from MEG data using ICA and mutual information.J Neurosci Methods. 2016 Aug 1;268:131-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 May 17. J Neurosci Methods. 2016. PMID: 27090949
-
EEG and MEG primers for tracking DBS network effects.Neuroimage. 2021 Jan 1;224:117447. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117447. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33059051 Review.
-
Characterizing the effects of deep brain stimulation with magnetoencephalography: A review.Brain Stimul. 2018 May-Jun;11(3):481-491. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2017.12.016. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Brain Stimul. 2018. PMID: 29331287 Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic review of MEG-based studies in Parkinson's disease: The motor system and beyond.Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Jun 15;40(9):2827-2848. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24562. Epub 2019 Mar 7. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019. PMID: 30843285 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal signal space separation for regions of interest: Application for extracting neuromagnetic responses evoked by deep brain stimulation.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Feb 1;45(2):e26602. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26602. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38339906 Free PMC article.
-
The comparative performance of DBS artefact rejection methods for MEG recordings.Neuroimage. 2020 Oct 1;219:117057. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117057. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 32540355 Free PMC article.
-
Robust detrending, rereferencing, outlier detection, and inpainting for multichannel data.Neuroimage. 2018 May 15;172:903-912. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.01.035. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 29448077 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetoencephalography for brain electrophysiology and imaging.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Feb 23;20(3):327-339. doi: 10.1038/nn.4504. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28230841 Review.
References
-
- Airaksinen K., Butorina A., Pekkonen E., Nurminen J., Taulu S., Ahonen A. Somatomotor mu rhythm amplitude correlates with rigidity during deep brain stimulation in Parkinsonian patients. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012;123(10):2010–2017. - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen K., Mäkelä J.P., Nurminen J., Luoma J., Taulu S., Ahonen A. Cortico-muscular coherence in advanced Parkinson's disease with deep brain stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014:S1388–S2457. - PubMed
-
- Brookes M.J., Vrba J., Robinson S.E., Stevenson C.M., Peters A.M., Barnes G.R. Optimising experimental design for MEG beamformer imaging. Neuroimage. 2008;39(4):1788–1802. - PubMed
-
- Cao C., Li D., Jiang T., Ince N.F., Zhan S., Zhang J. Resting state cortical oscillations of PD patients without and with subthalamic deep brain stimulation, a MEG study. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;32(2):109–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

