The role of insulin/IGF-1 signaling in the longevity of model invertebrates, C. elegans and D. melanogaster
- PMID: 26698870
- PMCID: PMC4915121
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.2.261
The role of insulin/IGF-1 signaling in the longevity of model invertebrates, C. elegans and D. melanogaster
Abstract
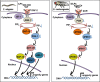
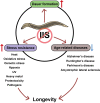
Insulin/insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 signaling (IIS) pathway regulates aging in many organisms, ranging from simple invertebrates to mammals, including humans. Many seminal discoveries regarding the roles of IIS in aging and longevity have been made by using the roundworm Caenorhabditis elegans and the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. In this review, we describe the mechanisms by which various IIS components regulate aging in C. elegans and D. melanogaster. We also cover systemic and tissue-specific effects of the IIS components on the regulation of lifespan. We further discuss IIS-mediated physiological processes other than aging and their effects on human disease models focusing on C. elegans studies. As both C. elegans and D. melanogaster have been essential for key findings regarding the effects of IIS on organismal aging in general, these invertebrate models will continue to serve as workhorses to help our understanding of mammalian aging. [BMB Reports 2016; 49(2): 81-92].
Figures
Similar articles
-
Untangling Longevity, Dauer, and Healthspan in Caenorhabditis elegans Insulin/IGF-1-Signalling.Gerontology. 2018;64(1):96-104. doi: 10.1159/000480504. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Gerontology. 2018. PMID: 28934747 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock factor 1 mediates the longevity conferred by inhibition of TOR and insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathways in C. elegans.Aging Cell. 2013 Dec;12(6):1073-81. doi: 10.1111/acel.12140. Epub 2013 Sep 4. Aging Cell. 2013. PMID: 23879233
-
Recent Progress in Regulation of Aging by Insulin/IGF-1 Signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Cells. 2022 Nov 30;45(11):763-770. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2022.0097. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 36380728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SMK-1, an essential regulator of DAF-16-mediated longevity.Cell. 2006 Mar 10;124(5):1039-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.12.042. Cell. 2006. PMID: 16530049
-
[Signal pathway of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) as a potential regulator of lifespan].Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol. 2008 Jan-Feb;44(1):3-11. Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol. 2008. PMID: 18411507 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Insulin Signaling Pathway Mediates FoxO-Pepck Axis Regulation of Glucose Homeostasis in Drosophila suzukii.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 27;25(19):10441. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910441. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408770 Free PMC article.
-
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus Probio-M9 extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans.Commun Biol. 2022 Oct 27;5(1):1139. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04031-2. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36302976 Free PMC article.
-
Innate sensitivity to stress facilitates inflammation, alters metabolism and shortens lifespan in a mouse model of social hierarchy.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Nov 9;11(21):9901-9911. doi: 10.18632/aging.102440. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31707362 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Phytochemicals with Anti-Aging and Lifespan Extending Potentials in Caenorhabditis elegans.Molecules. 2021 Dec 2;26(23):7323. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237323. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34885907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of mismatch repair in aging.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Sep 21;17(14):3923-3935. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.64953. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34671209 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee Y, An S, Artan M, et al. Genes and Pathways That Influence Longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans; in Aging Mechanisms, Mori N and Mook-Jung I (eds) Springer; Japan: (2015). pp. 123–169.
-
- Morris JZ, Tissenbaum HA, Ruvkun G. A phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase family member regulating longevity and diapause in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. (1996);382:536–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

