Resensitization to Crizotinib by the Lorlatinib ALK Resistance Mutation L1198F
- PMID: 26698910
- PMCID: PMC4773904
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1508887
Resensitization to Crizotinib by the Lorlatinib ALK Resistance Mutation L1198F
Abstract
In a patient who had metastatic anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged lung cancer, resistance to crizotinib developed because of a mutation in the ALK kinase domain. This mutation is predicted to result in a substitution of cysteine by tyrosine at amino acid residue 1156 (C1156Y). Her tumor did not respond to a second-generation ALK inhibitor, but it did respond to lorlatinib (PF-06463922), a third-generation inhibitor. When her tumor relapsed, sequencing of the resistant tumor revealed an ALK L1198F mutation in addition to the C1156Y mutation. The L1198F substitution confers resistance to lorlatinib through steric interference with drug binding. However, L1198F paradoxically enhances binding to crizotinib, negating the effect of C1156Y and resensitizing resistant cancers to crizotinib. The patient received crizotinib again, and her cancer-related symptoms and liver failure resolved. (Funded by Pfizer and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT01970865.).
Figures
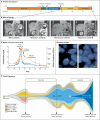

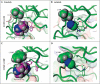
Comment in
-
Resistance: Crizotinib makes a comeback.Nat Rev Cancer. 2016 Feb;16(2):69. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.6. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26797648 No abstract available.
-
Lung cancer: Resolving resistance to ALK-targeted therapy.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016 Feb;13(2):64. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.8. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26806320 No abstract available.
-
Crizotinib Resensitization by Compound Mutation.N Engl J Med. 2016 May 5;374(18):1790-1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1601366. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 27144862 No abstract available.
-
Crizotinib Resensitization by Compound Mutation.N Engl J Med. 2016 May 5;374(18):1790. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1601366. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 27144863 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Crizotinib-Resistant ROS1 Mutations Reveal a Predictive Kinase Inhibitor Sensitivity Model for ROS1- and ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancers.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 15;22(24):5983-5991. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0917. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27401242 Clinical Trial.
-
Acquired resistance to the ALK inhibitor crizotinib in the absence of an ALK mutation.J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Mar;7(3):623-5. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318241daab. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22334013 No abstract available.
-
Identification of a novel T1151K ALK mutation in a patient with ALK-rearranged NSCLC with prior exposure to crizotinib and ceritinib.Lung Cancer. 2017 Aug;110:32-34. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2017.05.018. Epub 2017 May 22. Lung Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28676215
-
Overcoming crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged NSCLC with the second-generation ALK-inhibitor ceritinib.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016;16(2):147-57. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2016.1131612. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26654422 Review.
-
The accelerated path of ceritinib: Translating pre-clinical development into clinical efficacy.Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Apr;55:181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017. PMID: 28427013 Review.
Cited by
-
A case of primary pulmonary atypical carcinoid with EML4-ALK rearrangement.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21(1):12-16. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1665957. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31559892 Free PMC article.
-
Novel derivatives of anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors: Synthesis, radiolabeling, and preliminary biological studies of fluoroethyl analogues of crizotinib, alectinib, and ceritinib.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Nov 15;182:111571. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111571. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31425908 Free PMC article.
-
YAP1 mediates survival of ALK-rearranged lung cancer cells treated with alectinib via pro-apoptotic protein regulation.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 3;11(1):74. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13771-5. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31900393 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of using circulating tumor cells for detecting epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients: a meta-analysis and systematic review.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Mar 14;11:1373-1384. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S158479. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29559795 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Stage Shift and Population Mortality Among Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Dec 1;4(12):e2137508. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.37508. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34919136 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Druker BJ, Talpaz M, Resta DJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1031–7. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non–small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
